Category: Federal Legislation
We Need to Take Plastic Regulation More Seriously: Plastics as a Major Climate Change Contributor
Plastics are commonplace in modern society, despite increasing awareness of their negative environmental impacts. It is evident that plastic pollution litters our oceans and greenery, with devastating effects on natural ecosystems. Yet, the poor disposal of plastics is only part of the story—the production and management of plastics are incredible climate change contributors. Governmental action, however, has primarily focused on regulating the consumer and mitigating the impacts of plastics after use. Given the increasing urgency of climate change, it is time for the government to take the harm of plastics more seriously and regulate its production as the serious climate contributor it is.
The Plastic Problem
 Every year, between five hundred billion and one trillion plastic bags are used worldwide. (Jennie Reilly Romer, Comment: The Evolution of San Francisco’s Plastic-Bag Ban, 1 Golden Gate Univ. Envtl. L. J. 439, 439 (2007).) The average lifespan of a plastic bag is only twelve minutes. (Travis P. Wagner, Reducing single-use plastic shopping bags in the USA, Waste Management 70, 3, 4 (Sept. 2017).) This short lifecycle comes from a mix of user apathy and the fact that recycling plastics costs more than creating new plastics. (CIEL Report).
Every year, between five hundred billion and one trillion plastic bags are used worldwide. (Jennie Reilly Romer, Comment: The Evolution of San Francisco’s Plastic-Bag Ban, 1 Golden Gate Univ. Envtl. L. J. 439, 439 (2007).) The average lifespan of a plastic bag is only twelve minutes. (Travis P. Wagner, Reducing single-use plastic shopping bags in the USA, Waste Management 70, 3, 4 (Sept. 2017).) This short lifecycle comes from a mix of user apathy and the fact that recycling plastics costs more than creating new plastics. (CIEL Report).
Thus, the plastic or fossil fuel industry continues to produce new plastic, adding to greenhouse gas emissions with each item produced. “At current levels, greenhouse gas emissions from the plastic lifecycle threaten the ability of the global community to keep global temperature rise below 1.5°C degrees. By 2050, the greenhouse gas emissions from plastic could reach over 56 gigatons—10-13 percent of the entire remaining carbon budget.” (CIEL Report at 1.)
The Plastic Lifecycle
There are numerous reasons that plastics are considered to be major climate contributors. First, the substances used to make plastic, like ethylene and propylene, are derived from oil, gas, and coal, which must be extracted from the ground. (CIEL Report, at 21.) The combustion of these fuels and conversion of the petrochemicals each directly emit greenhouse gasses. (CIEL Report, at 44.)
Next, plastic production contributes indirectly to greenhouse gas emissions because the refining and manufacturing machines are powered by fossil fuels. (Id.). Currently, plastic production accounts for four to eight percent of global oil consumption every year and is projected to increase to about twenty percent by the year 2050. (CIEL Report, at 24). Studies have shown that for some plastics, the production process contributes up to sixty-three percent of the emissions in the plastic lifecycle. (Spyros Foteinis, How small daily choices play a huge role in climate change: The disposable paper cup environmental bane, 255 J. of Cleaner Production 1, 5 (Jan. 27, 2020)).
Further, some studies have attributed 37% of greenhouse gas emissions from plastics to management, or disposal processes. (Id.). Most plastic waste is put in a landfill. (CIEL Report, at 6). This is again because the cost of managing waste can often exceed the value of the materials that would be recovered from the recycling. (Wagner, at 5.) Additionally, plastic can only be “downcycled,” so single-use plastic can be of too poor quality to recycle. (Romer, at 446). As of 2017, only nine percent of all plastic discarded since 1950 has been recycled, and twelve percent incinerated. (CIEL Report, at 55).
Finally, some plastic is simply not managed. A portion of plastic is therefore just pollution. Such plastic often ends up in oceans and waterways, where it degrades slowly, releasing greenhouse gases and interfering with carbon sequestration. (Id.).
Current Regulation
Most current regulation deals with pollutant plastic, or plastic which has been used and discarded, causing obvious  environmental blight. Some cities and states have attempted to reduce plastic consumption by regulating the use of plastic bags. (Muhammad S. Khan et. al., Consumer green behaviour: An approach towards environmental sustainability, 28 Sustainable Development 5, 1019, 1168 (Oct. 8, 2020).). Local governments have also attempted to require the industry to invest in MSW management—thirty-three states have enacted extended producer responsibility (“EPR”) laws, which require producers to internalize some of the end-of-life costs of their products. (Wagner, at 3). Finally, localities often used unit-based pricing when picking up trash—but allow free recycling to incentivize residents to sort their own waste. (Id.).
environmental blight. Some cities and states have attempted to reduce plastic consumption by regulating the use of plastic bags. (Muhammad S. Khan et. al., Consumer green behaviour: An approach towards environmental sustainability, 28 Sustainable Development 5, 1019, 1168 (Oct. 8, 2020).). Local governments have also attempted to require the industry to invest in MSW management—thirty-three states have enacted extended producer responsibility (“EPR”) laws, which require producers to internalize some of the end-of-life costs of their products. (Wagner, at 3). Finally, localities often used unit-based pricing when picking up trash—but allow free recycling to incentivize residents to sort their own waste. (Id.).
However, these regulations generally focus only on regulating consumers rather than the plastics industry. Plastic bans incentivize a reduction in use, but only for a selection of plastics, at cost of the individual user. EPRs do regulate the plastic industry, but mainly forces the companies to internalize the economic cost, since the climate damage has already occurred by the time of disposal. Further, providing free recycling focuses solely on the consumer and does little to reduce the environmental cost given the lack of recycling that actually occurs and by again by focusing on only the end-of-life processes, after much of the climate damage has occurred.
It is therefore time for the government to take the greenhouse gas emissions over the plastic lifecycle more seriously, and work to reduce the production of plastics by directly regulating the plastics and fossil fuel industries—because they are the same thing.
Recommendations for the Future
The ideal environmental solution would be to reduce plastic manufacturing by setting limits on production; banning single-use plastic production and use; and stopping new oil, gas, and petrochemical infrastructure. (CIEL Report, at 82-83). Higher taxation on production could additionally achieve these reduction goals and incentivize the recycling of existing plastics. The federal and state governments could also adopt more stringent greenhouse gas emission targets and rigorously enforce them, including plastics in their calculations of emissions. (Id.)
Any of these solutions will be a political battle, however. The regulation of plastic has historically been impeded by the fossil fuel industry, which makes over four hundred billion dollars a year making plastic. Years of misinformation and court challenges by the fossil fuel industry have led to politicians shying away from plastics regulation. (See Jennie R. Romer & Shanna Foley, A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing: The Plastics Industry’s “Public Interest” Role in Legislation and Litigation of Plastic Bag Laws in California, 5 Golden Gate University Environmental Law J. 377, 381 (2012).).
Perhaps, then, the first step is simply to acknowledge the climate impact of plastics and increase public support of greater regulation to provide the political incentive. The lack of attention to this issue is evidenced by the fact that Biden’s “Executive Order on Tackling the Climate Crisis at Home and Abroad” does not even include the word plastic. This is an unacceptable reality if we ever hope to truly make climate progress. It is time for the government to take plastic regulation more seriously—we simply cannot afford not to.
 Meghan McCarthy anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2022.
Meghan McCarthy anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2022.
Fighting the Federal Government: California’s Mission to Stop Environmental Rollbacks
In July of 2020, California passed the historic Clean Trucking Rule, the first of its kind in the world. The rule requires manufacturers to sell increasing percentages of zero-emission trucks in the state. While many have applauded the action, the Trump administration was not a fan of the rule. California and the Trump administration have been at odds for years, as California has attempted to make up for the lack of climate action at the federal level. Over just four years, President Trump’s administration reversed over 100 environmental rules and regulations. To make up for the loss, California has passed numerous regulations and initiated at least twenty-four lawsuits to halt the Environmental Protection Agency’s (“EPA”) rollbacks. California, given its unique legal status on environmental issues, has proven itself to be a clear leader on climate action and emission reduction.
The Clean Air Act
When it comes to the climate, California is not restricted by Constitutional provisions such as the Commerce and Preemption Causes. The Clean Air Act (“CAA”), first passed in 1970, gives the federal government the ability to regulate pollutants that are emitted into the ambient air and prohibits states from adopting or attempting to enforce any of their own motor vehicle emission controls. However, section 209(b) of the CAA allows states that had adopted standards prior to 1966 could apply for a waiver to that prohibition; and only California qualified. California was the first state to attempt controlling auto pollution and needed the ability to adopt more stringent controls to address the state’s extreme smog problem. To set new motor vehicle emissions standards, California must apply for a waiver from the EPA. The EPA administrator shall grant the waiver unless the standard is (1) arbitrary and capricious, (2)is not needed for compelling and extraordinary conditions, or (3) is not consistent with the CAA. Since 1970, administrators have consistently granted California its waivers. One exception was a waiver for new emissions restrictions on vehicles starting in 2009 that was initially denied in 2008, but President Obama later reversed the denial. This waiver program has created numerous California programs that differ from federal standards, including the Zero Emissions Vehicles (“ZEV”) Program, The Advanced Clean Cars program, and Low Emission Vehicles (“LEV”) Standards.
Under section 177 of the CAA, other states can choose to adopt either the current federal regulations or the California regulations if that will help the state achieve the CAA requirements more efficiently. As of August 2019, fourteen states have adopted portions of California’s ZEV and LEV programs.
California’s New Rule
The California Air Resources Board (“CARB”) established the Advanced Clean Truck Program. The program requires that
beginning in 2024 manufacturers sell zero-emission trucks— that is electric and fuel cell powered trucks—as an increasing percentage of their annual California sales. Zero emission trucks need to make up 55% of Class 2b – 3 truck sales, 75% of class 4 – 8 straight truck sales, and 40% of truck tractor sales by 2035. Massachusetts and seven other states have pledged to follow California’s lead for medium and heavy duty trucks. Additionally, fifteen states and Washington D.C. have signed a memorandum of understanding pledging to each develop an action plan to support widespread electrification of medium and heavy duty vehicles.
With these monumental steps forward, the federal government started to push back. The Trump EPA and National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (“NHTSA”) issued a final rule titled the “One National Rule Program,” which finalized parts of the Safer, Affordable, Fuel-Efficient (“SAFE”) Vehicles Rule that was first proposed in August 2018. The action makes clear that federal law preempts state and local tailpipe greenhouse gas emissions standards as well as ZEV mandates. As soon as President Biden took office, however, he ordered federal agencies to reexamine these changes.
The EPA and California’s Rule
 The California rule is set to take effect in 2024, but a waiver must be approved by the EPA beforehand. The EPA has never gone through a denial of a California waiver before, but that has not stopped the Trump Administration from trying to revoke previously granted waivers for zero emission passenger vehicle standards. The EPA is pursuing the revocation of California’s 2013 preemption waiver for greenhouse gas emissions and ZEV programs. This revocation is currently being challenged in court. If former President Trump won the 2020 election, the EPA may have tried to deny California’s zero emission truck regulations waiver. The EPA, however, would have faced an uphill battle because there is clear evidence that reducing emissions is necessary to help California achieve its CAA goals. California’s argument would have been bolstered by the recent wildfires that destroyed large swaths of the state. It was unlikely the EPA could have offered enough solid evidence to uphold their waiver denial. In addition, most legal experts agree that California, and the states that follow their regulations, had a strong case that the Trump Administration’s efforts were unlawful. Still, the changing balance on federal appeals courts and the Supreme Court could undermine California’s waiver process and spell the demise of the original purpose and intent of the CAA. For the time being, however, California and allied states continue to have a valuable tool to fight climate change and reduce emissions across the entire nation regardless of who controls the EPA.
The California rule is set to take effect in 2024, but a waiver must be approved by the EPA beforehand. The EPA has never gone through a denial of a California waiver before, but that has not stopped the Trump Administration from trying to revoke previously granted waivers for zero emission passenger vehicle standards. The EPA is pursuing the revocation of California’s 2013 preemption waiver for greenhouse gas emissions and ZEV programs. This revocation is currently being challenged in court. If former President Trump won the 2020 election, the EPA may have tried to deny California’s zero emission truck regulations waiver. The EPA, however, would have faced an uphill battle because there is clear evidence that reducing emissions is necessary to help California achieve its CAA goals. California’s argument would have been bolstered by the recent wildfires that destroyed large swaths of the state. It was unlikely the EPA could have offered enough solid evidence to uphold their waiver denial. In addition, most legal experts agree that California, and the states that follow their regulations, had a strong case that the Trump Administration’s efforts were unlawful. Still, the changing balance on federal appeals courts and the Supreme Court could undermine California’s waiver process and spell the demise of the original purpose and intent of the CAA. For the time being, however, California and allied states continue to have a valuable tool to fight climate change and reduce emissions across the entire nation regardless of who controls the EPA.
 Conner Kingsley anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
Conner Kingsley anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
Shifting Baselines are a Double-Edged Sword: Why Climate Advocates Must Honor Our Environmental Laws In Shaping Climate Policy
In his 1970 state of the union address, Richard Nixon said, “we still think of air as free. But clean air is not free, and neither is clean water. The price tag on pollution control is high. Through our years of past carelessness, we incurred a debt to nature, and now that debt is being called. The program I shall propose to Congress will be the most comprehensive and costly program in this field in America’s history.” President Nixon later signed bipartisan legislation establishing Environmental Protection Agency.
EPA efforts implementing laws such as the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act have greatly reduced pollution throughout the United States. Enforcement of the CAA has reduced aggregate national emissions of the six common pollutants by 73 percent. At the same time, gross domestic product grew by 324 percent. The CWA has had a rockier implementation – Flint Michigan still doesn’t have clean water – but has nevertheless had a significant impact on reducing water pollution.
United States. Enforcement of the CAA has reduced aggregate national emissions of the six common pollutants by 73 percent. At the same time, gross domestic product grew by 324 percent. The CWA has had a rockier implementation – Flint Michigan still doesn’t have clean water – but has nevertheless had a significant impact on reducing water pollution.
Unfortunately, Americans are already forgetting that clean air and clean water is not a guarantee or a constitutional right, due in part to the phenomenon known as shifting baseline syndrome. It suggests that something that was abnormal in the past, becomes the new normal, or baseline, for a generation of individuals, who then collectively forget the past baselines.
First explained in 1995, this cognitive theory has gained traction in the climate community to explain public antipathy towards action on climate change. It suggests that as average temperatures and associated climate effects slowly increase over time, individuals will fail to recognize the danger that the climate crisis poses, and collective action may fail to materialize as a result. Climate activists fear that no specific event will motivate action similar to the environmental crises in the 1970’s, and like a lobster in a pot of boiling water, we won’t realize what is happening until it is too late.
 Shifting baselines, however, are not limited to present climate effects, but also work to undermine public support for current environmental laws and regulations that continue to reduce pollution in the present day. In 1995, for example, EPA embarked on an ambitious project to cure 400 years of environmental degradation and make the Charles River swimmable and fishable again, pursuant to its authority under the Clean Water Act. While those goals have not fully been achieved – EPA does not advise swimming on some days, and fishermen can only catch, then release fish – the monumental efforts have reduced source pollution from raw sewage flows and have led to a 99.5% reduction in source contributions to the river.
Shifting baselines, however, are not limited to present climate effects, but also work to undermine public support for current environmental laws and regulations that continue to reduce pollution in the present day. In 1995, for example, EPA embarked on an ambitious project to cure 400 years of environmental degradation and make the Charles River swimmable and fishable again, pursuant to its authority under the Clean Water Act. While those goals have not fully been achieved – EPA does not advise swimming on some days, and fishermen can only catch, then release fish – the monumental efforts have reduced source pollution from raw sewage flows and have led to a 99.5% reduction in source contributions to the river.
As a transplant to Boston, I was shocked to learn that the Charles has such a toxic history. And it is possible, if not probable, that an entire generation of Bostonians will grow up taking this privilege for granted. It may even be easy, based upon the unqualified success of the river cleanup, to forget the substantial sacrifices made and costs incurred in restoring the Charles.
This intergenerational failure to maintain understanding of past action in an environmental context may present a barrier to action on climate change. If the public discounts past costs to safeguard our water and air or the costs of maintaining environmental quality, the harder it will be to take new action. The public will not be ready to accept the significant costs required to tackle the climate crisis.
This is why it is imperative for climate advocates to not discount our existing environmental laws, but to actively celebrate their successes. It is incumbent on our present leaders and policymakers to stress how far we have come to clean the environment. They must frankly and openly discuss the means we took to get here. And they must stress that it is in our power to once again make the difficult decision to invest time, energy, and significant sums of money to clean our environment. We are not working from a blank slate in the climate fight.
Unfortunately, it seems that even our legislators pursuing climate action view climate solutions as separate and distinct from the long history of environmental action. For example, the Green New Deal discusses the World War II and New Deal mobilizations but fails to mention the bedrock environmental laws of the 1970s or the decades of subsequent pollution abatement.
We face severe environmental and public health challenges. We are not on track to keep global temperatures below 2 degrees Celsius. Sea level rise threatens our coasts. Ocean acidification will virtually eliminate all coral reefs and their priceless biodiversity and threaten coastal fishing communities’ livelihoods. It may be easy to abhor the cost of action, but we have not only known for fifty years of the cost of a clean, resilient, and sustainable environment, we accepted those sacrifices. It is time to embrace that history, rather than run from it.
 Joshua Williams anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
Joshua Williams anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
There’s No Such Thing as Sex Without Consent
On January 16, 2020, the Massachusetts Senate passed S.2475 “An Act Relative to Healthy Youth,” which creates mandatory guidelines schools must follow when implementing their sex education curricula. This does not require schools to adopt a curriculum, and there is an opt-out provision for parents who do not wish their children to receive this education. Still, the bill requires medically accurate information be shared, that a comprehensive view of sex education be taught that goes beyond abstinence-only education, and, perhaps most importantly, the bill requires schools teach students about consent, boundaries, and healthy and safe relationships. Unfortunately, the 2020 legislative session came to an end with the bill stuck in the House Committee on Ways and Means.
Sex Education in the United States
In the United States, sex education started as a movement to discourage masturbation in young men, and encourage abstinence before marriage. While sex education started to spring up more in public schools during the 1920s, it wasn’t until the 1950s when the the American Medical Association and public health officials first advocated a standardized curriculum. The 1960s saw religious and conservative groups attack sex education, asserting that teaching youths about sex would make sexual engagement more likely. In the 1980s, the HIV/AIDS health crisis led many officials, backed by federal funding, to require abstinence-only sex education in schools.
before marriage. While sex education started to spring up more in public schools during the 1920s, it wasn’t until the 1950s when the the American Medical Association and public health officials first advocated a standardized curriculum. The 1960s saw religious and conservative groups attack sex education, asserting that teaching youths about sex would make sexual engagement more likely. In the 1980s, the HIV/AIDS health crisis led many officials, backed by federal funding, to require abstinence-only sex education in schools.
By 2009, the federal government was putting $170 million per year into these George H.W. Bush era programs. Under President Obama, the federal government continued funding abstinence-only programs, but also introduced a more comprehensive sex-education approach in an effort to reduce teen pregnancy. The Trump administration then gutted the Teen Pregnancy Prevention Program, restricting federal funding to abstinence-only programs.
On the state level, 37 states require sex education programs to cover abstinence and 27 of those require prioritizing abstinence. 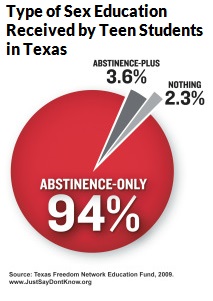 Students who attend schools with less funding are more likely to receive abstinence-only education, leading to a correlation between socioeconomic status and an increase in teen pregnancy, STDs, and sexual violence.
Students who attend schools with less funding are more likely to receive abstinence-only education, leading to a correlation between socioeconomic status and an increase in teen pregnancy, STDs, and sexual violence.
Currently, only 8 states and Washington D.C. require students learn about consent. Of these, seven passed their requirements within the last four years. In just 2019, four jurisdictions passed consent education requirements and nine more states introduced similar legislation.
The Importance of Consent Education
Sex is not sex without consent – it’s rape.
A Columbia University study indicated that those who received training in how to refuse sexual advances were less likely to be sexually assaulted in college. There was no similar correlation between abstinence-only sex education and sexual assault. Equipping students with the ability to set their own boundaries is important, but teaching students to recognize and respect those boundaries in others is just as necessary to prevent sexual violence. Merely giving students the tools to help them potentially get out of a situation they don’t want to be in is not enough, because it does not express the importance of consent in sexual interactions. As long as people fail to recognize and respect the consent of others, there will always be uncomfortable or dangerous situations to try to get out of – it’s mopping up the water from the overflowing sink without turning off the tap.
For young children, consent education reassures them that they have a say in what happens to their bodies (something many children are not aware of), and it teaches them to respect other peoples’ choices, as well. As students age, understanding consent as a concept allows them to form fundamental understandings of what healthy relationships with others look like. Beyond a reduction in sexual violence and misconduct, these are important life-skills that reach far beyond sexual situations.
The Opposition
There is still support for abstinence-only sex education in many parts of the country, and consent education is often seen as condoning sex. Unfortunately, resisting consent education works against abstinence-only goals by not providing students with the tools needed to establish healthy boundaries and respect for each other’s physical space. These skills are key for both those who wish to remain abstinent until marriage and for those who engaging in sex.
condoning sex. Unfortunately, resisting consent education works against abstinence-only goals by not providing students with the tools needed to establish healthy boundaries and respect for each other’s physical space. These skills are key for both those who wish to remain abstinent until marriage and for those who engaging in sex.
Some of those who oppose consent education, especially for younger students, worry that the subject matter may be too mature, but consent education does not have to be presented along with sex education for younger students to be effective. Consent is ultimately about permission, which is a concept children can easily grasp. For example, sharing and borrowing things involves consent. Additionally, teaching consent around hugging is a way to instill physical boundaries in children.
Looking Forward
West Virginia, Rhode Island, and D.C. have all adopted comprehensive legislation on consent education. These states require consent education based on the student’s age, introduce the concept of consent to younger children while assuaging some of the opponent’s concerns.
Harvard’s Graduate School of Education created a consent education model based on suggestions from educators across the country. The model proposed laying a foundation of consent and boundary building behaviors in younger children, and then including sex in the conversation for older students.
The Harvard model also recognizes that consent education should not be limited to straight boys but that anyone can perpetrate sexual violence and misconduct. Just as socioeconomic factors play a role in who receives comprehensive sex education, individuals holding certain identities are disparately impacted by sexual violence and students need to be aware of these inequities as they learn to navigate sex and consent.
Every school should adopt some form of consent education both before and during sex education. Otherwise, we will continue to endure a society that fails to respect the boundaries and choices of others. The Massachusetts Senate passed bill was a step in the right direction. Hopefully, the bill will become law during this new legislative session.
 Alexa Weyrick anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
Alexa Weyrick anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
The Real Cost of COVID-19: The Fractured Health Care System
The coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has uprooted the very foundation everyday life, turning socialization into a moral evil, and weaponizing safety precautions as political propaganda. These clear immediate costs, amounting in the loss of life, jobs, and social pleasures, are merely the surface to a rather elaborate system of institutional market failures that are bound to follow. While the coronavirus promptly began a long-awaited economic recession, forcing more than 31 million people in the United States to file for unemployment insurance, there has been a catastrophic loss of employer based health insurance coverage for many individuals, leaving only those who are eligible and qualified to move over to Medicaid or other subsidized health insurance policies. Unfortunately many have found themselves stuck in what is known as the “coverage gap,” with health care access becoming a novelty when its demand is at an all-time high.
Hospital and Insurance Coverage Crisis
Hospitals are largely believed to be price inelastic institutions, where demand for health services will remain constant, and funds will continuously keep providers operational even during economic recessions. While one might think that the COVID-19 public
health crisis would drive health care consumption, benefiting hospitals, it has actually been quite the opposite. Demand for healthcare services has been primarily for expensive specialized care, imposing high out-of-pocket expenses on individuals who are treated for COVID-19, and has further shifted from routine visits, seeing reductions as high as 60%.. The increased costs in specialized care, combined with the decrease in less costly routine care has not been the only shock to the health care industry. Additionally, by April of 2020, 1.4 million health care jobs were lost to enable hospitals to produce positive profit margins, creating staffing shortages across many US hospitals. This, paired with over 40 million Americans losing their jobs and shifting to subsidized healthcare and Medicaid, has created a loss of up to 20% of the commercial insurance market. By decreasing those covered by commercial insurance plans, cost aversion behaviors will decline health care usage, and those who are eligible will move over to Medicaid. Shifting from private to public insurance at this rate will cost Hospitals $95 billion in annual revenue. While Hospitals are experiencing adverse pressure, threatening what was believed to be recession proof industry, it is merely one of the many cracks that make up an unsustainable health care system.
The CARES Act and FFCRA’s Truncated Effect on the Health Care Crisis.
The passage of both the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (“CARES Act”) and the Families First Coronavirus Response Act (“FFCRA”) has provided economic stimulus and safety protocols to expand health care access. These measures have covered COVID-19 diagnostic testing, mandating the elimination of cost-sharing, such as co-payments, deductibles, and coinsurance, for a wide array of group health plans and insurances. While this improves accessibility to preventative measures, it leaves open a large regulatory gap for the actual treatment of COVID-19, where individuals are still vulnerable to out-of-pocket expenses until they reach their cap for insurance to kick in, “ exceeding “$8,000 for an individual and $16,000 for a family.” The benefit of expanding access to testing is immeasurable, but the high costs of treatment poses a significant risk to those who are already underinsured. Further, these acts fail to eliminate cost-sharing for the uninsured, which accounts for 27.9 million nonelderly individuals in the US in 2018. While the number of uninsured Americans is certainly alarming, it is a great improvement from the number of uninsured prior to the enactment of the Affordable Care Act (“ACA”), where over 46.5 million nonelderly individuals were uninsured in 2010. Yet, the many positive effects that have followed the enactment of the ACA are at risk of being undone, with the Supreme Court of the United States reviewing four legal questions pertaining to the ACA.
The Uncertainty of Health Care in the face of California v. Texas.
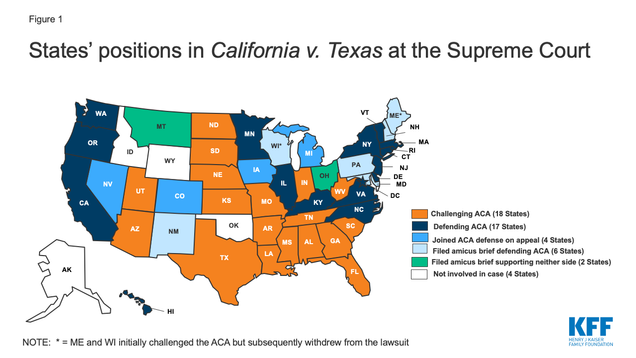 California v. Texas will be a test to the legislative muster of the ACA. With the recent confirmation of Justice Amy Coney Barrett to the Supreme Court, concerns of the ACA being overruled have surfaced as Justice Barrett has claimed that Chief Justice Roberts has “pushed the Affordable Care Act beyond its plausible meaning to save the statute.” The fate of the ACA hinders on whether the individual mandate is unconstitutional, and if so, if the individual mandate of the ACA is severable from the rest of the legislation. If the court does decide to overrule the ACA in its entirety, we may see more than 20 million individuals lose health care insurance, exacerbating the already grim public health crisis brought on by COVID-19, impacting our most vulnerable communities who struggle to gain access to health care.
California v. Texas will be a test to the legislative muster of the ACA. With the recent confirmation of Justice Amy Coney Barrett to the Supreme Court, concerns of the ACA being overruled have surfaced as Justice Barrett has claimed that Chief Justice Roberts has “pushed the Affordable Care Act beyond its plausible meaning to save the statute.” The fate of the ACA hinders on whether the individual mandate is unconstitutional, and if so, if the individual mandate of the ACA is severable from the rest of the legislation. If the court does decide to overrule the ACA in its entirety, we may see more than 20 million individuals lose health care insurance, exacerbating the already grim public health crisis brought on by COVID-19, impacting our most vulnerable communities who struggle to gain access to health care.
Disparities on Minority Care and COVID-19 Infection.
Racial and ethnic minority groups face the greatest barriers to health care access, and, in turn are more likely to be uninsured or underinsured compared to their non-Hispanic white counterparts. While the ACA had greatly reduced the proportion of racial and ethnic minorities who lack health insurance, there are numerous systemic and social hurdles that have left these minority groups uninsured at higher rates than white individuals. As a consequence, racial and minority groups have been disproportionately affected by COVID-19, with racial minorities being over 2.6 times as likely to contract COVID-19, with rate of hospitalization for African American individuals being 4.7 times more than that of white individuals. Not only this, but the mortality rate is 2.1 times that of white people in the US, showing clear disparity in treatment outcomes and access to treatment.
The disproportioned access to health care services from racial and ethnic minority groups, has undoubtedly put these individuals at higher risk to unexpected out-of-pocket expenses, surprise bills, and physical harm from COVID-19. COVID-19 has shed light on the systemic racism in our health care system, unfortunately adding to the already disastrous public health crisis. The many cracks that are forming throughout our health care system will have untold effects on minority populations, and needs to be addressed through comprehensive legislative health care reform that is aimed at providing universal insurance coverage and eliminating implicit biases that contribute to lower standard care.
While the sprawling costs of COVID-19 stand out as clear reminders that we are living anything but a normal life, the true long term costs on minority populations, health care institutions, and health care access is now even more clear as Americans face another wave of COVID-19 outbreaks during these colder months. This cocktail of failures will greatly impact an already fragmented health care system, leaving our most vulnerable communities without proper health care access. Congress and the state legislatures need to secure funding for the providers of our health care services, while also increasing access to health care insurance and treatment for all individuals to minimize the long-term costs associated with COVID-19.
 Kyle Hafkey anticipates graduating from Boston University Schoo of Law in May 2022.
Kyle Hafkey anticipates graduating from Boston University Schoo of Law in May 2022.
What Never Was: The Indigenous American Cultural Heritage Repatriation Problem
The unfortunate beginnings of the fetishization of Indigenous American cultural heritage occurred concurrently with the systematic disenfranchisement of Native Americans throughout the United States. These events led to the amassing of millions of Indigenous American cultural heritage objects in federal repositories, museums, and private collections by the early twentieth century. Concurrently, archaeologists and anthropologists, largely funded by public research institutions like museums and universities, thoroughly destroyed prehistoric and historic sites in the hunt of the next ancient relic. The culmination of these events as well as forced assimilation created the idea that Indigenous Americans vanished and further justified the amassing of their cultural heritage. Unfortunately, today’s global society still believes in the vanishing Indian.
The Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act (“NAGPRA”) was supposed to protect the heritage of the Indigenous Americans, but it is deeply flawed and needs to be either amended or replaced.
CONGRESS’S RUSHED RESPONSE TO CONTROVERSY
The Supreme Court ruled in Lyng v. Northwest Indian Cemetery Protection Association that the American Indian Religious Freedom Act (“AIRFA”), 42 U.S.C. § 1996, merely reiterates the First Amendment. Thus, the U.S. Forest Service (“USFS”) continued with road construction after minimizing the immediate impacts to the Yurok’s, Karok’s, and Tolowa’s religious practices. After the decision, the Indigenous American community knew they needed heightened protections, and the Senate Select Committee on Indian Affairs concluded that federal legislation was necessary. On the heels of the committee findings, federal legislation was drafted and enacted. NAGPRA was supposed to positively affect the acquisition and repatriation of Indigenous American ancestral remains and cultural heritage.
Congress enacted NAGPRA to protect Indigenous American graves and repatriate remains, providing for proper tribal burials and religious rites. Although the legislative history suggests good intentions, the federal legislation provides a façade for museums, galleries, and collectors to continue acquiring and exhibiting Indigenous American cultural heritage. NAGPRA, enacted in November of 1990 and effective a year later, requires federal agencies and institutions benefiting from federal funding that have “possession or control over holdings or collections of Native American human remains and associated funerary objects [to] compile an inventory of such items and, to the extent possible based on information possessed by [the agencies and institutions, to] identify the geographical and cultural affiliation of such items.” From here, institutions and federal agencies inventory their collections “in consultation with tribal government [officials]. . . and traditional religious leaders” and supply records for better determining “the geographical origin, cultural affiliation, and basic facts surrounding [the] acquisition and accession of Native American human remains and associated funerary objects . . . .” “If a ‘cultural affiliation of Native American human remains and associated funerary objects’ is established with a particular tribe, then ‘upon the request of a known lineal descendant of the Native American or of the tribe[,]’ the museum must ‘expeditiously return such remains and associated funerary objects.’”
WHY NAGPRA FAILS
NAGPRA is but one illustrious example of the federal government fostering conflict between Indigenous American religion and Eurocentric ideals of science. While religion and science both concern themselves with “the human identity and defining our place in the universe,” their methods employed to achieve these goals often conflict. Science utilizes deductive methodology emphasizing quantifiable information and discernible facts and leads to evidence-based conclusions. Region supports discovery through “faith, complex belief systems, and longstanding traditions supported by cultural awareness.” The answer is not and never has been one practice over the other, and America’s past placed Congress in an important decision-making role to efficiently incorporate both viewpoints. What Congress enacted is neither effective nor efficient legislation, but an all show, no substance process.
NAGPRA leans heavily in favor of Eurocentric ideals of science over Indigenous American religious freedoms and oral history. Nevertheless, Congress failed at greatly considering the issue’s greatest stakeholder—Indigenous Americans. While Congress heard the religious perspective from tribal government representatives, lineal descendants, and various other support groups, the followed in-practice NAGPRA guidelines suggest their perspective fell on deaf ears.
Indigenous Americans view funerary, sacred, and cultural patrimony objects as the extensions of once-living ancestors, and therefore deserving of the same protections afforded to ancestral remains. Treating these objects as anything less offends Indigenous American cultural practices, and disturbances “force the spirits of those individuals to wander without rest.” The scientific viewpoint sees historical and scientific value in ancestral remains and their associated objects. Bioanthropologists premise their work around these objects and remains, hoping to learn more about past and present populations as well as information about the individual ancestral remains. Bioanthropologists swayed Congress with their wishes to retain ancestral remains for future study, supporting their argument by suggesting future technologies might provide unknown answers. Of course, Indigenous Americans’ oral histories provide the answers, but the judiciary and bioanthropologists brushed those claims aside. Thus, scientists and Indigenous Americans remain on polar extremes—“either believing in continued possession for research purposes or insisting on immediate burial without study.” Congress enacted NAGPRA with a focus on the repatriation of ancestral remains and associated objects. Yet, the rushed and sloppy NAGPRA legislation contains loopholes and lacks enforcement mechanisms.
Existing Loopholes
NAGPRA falls flat when repatriating cultural heritage not culturally identifiable and not traceable to a contemporary and federally-recognized tribe. These limitations result in 73% of remains remaining in museum collections because they were deemed non-affiliable and not repatriable. “[T]he unaffiliated remains of more than 115,000 individuals and nearly one million associated funerary objects have sat on museum shelves in legal purgatory.” A March 2010 amendment, Disposition of Cultural Unidentifiable Human Remains, attempted to redress these limitations. Before the amendment’s enactment, a majority of ancestral remains were classified as non-affiliable and outside NAGPRA’s initial scope.
NAGPRA, in its current state, fails on multiple fronts. First, the amendment addresses unaffiliated ancestral remains, but does

(© President and Fellows of Harvard College, Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology, [24-15-10/94603 + 60740377])
Mimbres bowls, produced by people living in the Southwest from the late 10th to early 12th century A.D., are renowned for the unique imagery found on their interiors. The black-on-white ceramics were often decorated with geometric patterns.
not resolve the issue with funerary and sacred objects such as Mimbres bowls. Second, NAGPRA requires museums, federal agencies, and public institutions to consult with tribal governments in determining affiliation and recommendations of repatriation, yet this important step rarely occurs. Third, cultural affiliation rests upon the interpretation of a preponderance of evidence determined by the same collection of museums, federal agencies, and public institutions retaining the Indigenous American cultural heritage. Fourth, only federally-recognized tribes may bring repatriation claims, thus eliminating hundreds of tribes awaiting or denied federal recognition. Fifth, NAGPRA only applies to federally-funded institution and federal agency collections. Consequently, federally-funded institutions receiving promised gifts and loans from private collections circumvent NAGPRA responsibilities. Finally, NAGPRA established the Committee, made up of seven members, which reviews repatriation claims when requested by any of the involved parties. However, the Committee merely publishes non-binding advisory findings. Language not clearly explained by Congress can be reasonably interpreted by federal agencies provided they give adequate explanations, and thus provides major deference to agency decisions. Therefore, the current loopholes allow federal agencies and federally-funded institutions to act as the decision makers for repatriation claims, and leads to biased outcomes against the marginalized Indigenous American tribal communities.
Lacking Enforcement Mechanisms
Congress limited NAGPRA’s effectiveness by omitting dissuasive penalties for federal agencies and federally-funded institutions. In fact, the legislation is completely silent on penalties towards federal agencies. Subsequently, most federal agencies have not completed collection inventories, a process required to place tribes on notice of NAGPRA-protected cultural heritage and ancestral remains. NAGPRA required completed inventories no later than November 16, 1995, yet the Department of the Interior’s (“DOI”) agencies have failed at cataloging over 78 million cultural heritage objects and ancestral remains. Thus, tribal governments cannot place repatriation claims and have no course of action for dispute settlements.
The DOI’s Secretary assesses civil penalties to federally-funded institutions who fail to comply with NAGPRA. Nevertheless, federally-funded institutions frequently circumvent any penalties if they reasonably explain their decisions not to repatriate based on a preponderance of the evidence, regardless of the Committee’s recommendations. Legislation without adequate enforcement measures leaves agencies and institutions with too much power and tribal governments incapable of obtaining the just and fair outcomes sought.
For Indigenous Americans, NAGPRA continues to fail and fall flat on Congress’s goals thirty years later. Improper interpretation of NAGPRA and unfair results will continue without reconsidering the current legislation and elaborating upon the ambiguities. Next session, Congress should, at the very least, take action to close the NAGPRA's loopholes and add meaningful penalties. Even better, it should take this opportunity to completely rethink its approach to restoring and protecting the sacred objects of Indigenous Americans.
Tyler Heneghan anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
Disparate Impact in Machine Learning
Machine learning or “AI” is a novel approach to solving problems with software. Computer programs are designed to take large amounts of data as inputs, and recognize patterns that are difficult for humans to see. These patterns are so complex, it is sometimes unclear what parts of the data the machine is relying on to make a decision. This type of black box often produces useful predictions, but it is unclear whether the predictions are made based on forbidden inferences. It is possible that machine learning algorithms used in banking, real estate, and employment rely upon impermissible data related to protected classes, and therefore violate fair credit, housing, and labor laws.
Machine learning, like all programmed software, follows certain rules. The software generally compares images or numbers with
descriptions. For instance, facial recognition software may take as inputs pictures of faces, labeled with names, and then identify patterns in the face to associate with the name. Once the software is trained, it can be fed a picture of a face without a name, and the software will use the patterns it has developed to determine the name of the person that face belongs to. If the provided data is accurately prepared and labeled, the software usually works. If there are errors in the data, the software will learn the wrong things--and be unreliable. This principle is known as “garbage in, garbage out”--machine learning is only ever as reliable as the data it works with.
This causes problems when machine learning is applied to data that has racial bias baked-in to its core. Machine learning has been used in the criminal justice system to purportedly predict--based on a lengthy questionnaire--whether a perpetrator is likely to reoffend. The software was, after controlling for arrest type and history, 77% more likely to wrongfully predict that black defendants would re-offend than white defendants. Algorithms used by mortgage lenders charge higher interest rates to black and latino borrowers. A tenant screening company was found to rely partly on “arrest records, disability, race, and national origin” in its algorithms. When biases are already present in society, machine learning spots these patterns, uses them, and reinforces them.
 There are two ways of interpreting the racial effect of machine learning under discrimination law: disparate treatment and disparate impact. Disparate treatment is fairly cut-and-dry, it prohibits treating members of a protected class differently from members of an unprotected class. For instance, giving a loan to a white person, but denying the same loan to a similarly situated black person, is disparate treatment. Disparate impact is using a neutral factor for making a decision that affects a protected class more than an unprotected class. Giving a loan to a person living in a majority-white zip code, while refusing the same loan to a similarly situated person living in a black-majority zip code, creates a disparate impact.
There are two ways of interpreting the racial effect of machine learning under discrimination law: disparate treatment and disparate impact. Disparate treatment is fairly cut-and-dry, it prohibits treating members of a protected class differently from members of an unprotected class. For instance, giving a loan to a white person, but denying the same loan to a similarly situated black person, is disparate treatment. Disparate impact is using a neutral factor for making a decision that affects a protected class more than an unprotected class. Giving a loan to a person living in a majority-white zip code, while refusing the same loan to a similarly situated person living in a black-majority zip code, creates a disparate impact.
Whether machine learning creates disparate treatment, disparate impact, or neither, depends on the lens the system is viewed through. If the software makes a decision based on a pattern that is the machine equivalent to protected class status, then it is committing disparate treatment discrimination. If a lender uses the software as its factor in deciding whether to grant a loan, and the software is more likely to approve loans to unprotected class members than it is to approve loans to similarly situated protected class members, then the lender is committing disparate impact discrimination. And if a lender uses software that relies on permitted factors, such as education level, yet nevertheless winds up approving more loans for unprotected class member than it does for protected class members, the process could be discriminatory but not actionable under either disparate treatment or disparate impact theory.
The problem thus depends in part on understanding how the machine interprets the data--the exact information we often lack when machine learning is particularly complex. Thus, instead of relying on either disparate impact or disparate treatment theory, perhaps legal analysis of discrimination in machine learning should be entirely outcomes-driven. If, in fact, an algorithm wrongly predicts the likelihood of an event occurring, and that algorithm is less accurate for protected class members than unprotected class members, the algorithm should be considered prima facie discriminatory. Such a solution is viable for examining recidivism, interest rates and loan repayment, but it may be insufficient to cover problems like housing denials or employment. If an algorithm denies protected class members access to housing in the first place, it is difficult to falsify the algorithm’s decision, as nonpayment or other issues necessarily do not arise.
Machine learning offers great promise to escape the racial biases of our past if it is programmed to only rely on neutral factors. Unfortunately, it is currently impossible to determine which factors used by machines are truly neutral. Improperly configured machine learning has led to higher incarceration rates for black inmates and higher loan interest rates for black and latino homeowners. Such abuses of machine learning technology must be rejected by the law.
 Schecharya Flatté anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
Schecharya Flatté anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
Telehealth in the Era of COVID-19 and Beyond
Governor Charlie Baker of Massachusetts has recently issued an Order Expanding Access to Telehealth Services and to Protect Health Care Providers. The order, issued in March, is a public health response to the state’s state of emergency due to the Coronavirus or COVID-19 outbreak. Under the order, the Group Insurance Commission, all Commercial Health Insurers, Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Massachusetts, Inc. and health maintenance organizations regulated by the Division of Insurance are required to let all in-network providers deliver clinically appropriate, medically necessary covered services to their members via telehealth, and to mandate reimbursement for these services. The purpose behind the Order is to encourage the use of telehealth in the mainstream of health care provision, as a “legitimate way for clinicians to support and provide services to their patients.”
Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Massachusetts has recorded over half a million patient telehealth visits over a six-week span and that number is only increasing with time. In comparison, the average number of telehealth visits before the COVID-19 pandemic was 5,000. The demand for health care and medical advice without the requirement of an in-person appointment has soared in light of the outbreak that prevents or prohibits people from attending one due to social distancing guidelines. Prior to the crisis posed by the pandemic and before Governor Baker’s order, hospitals and doctors were disincentivized from offering telehealth visits because health insurers did not cover them or would offer a smaller pay as compared to in-person visits. By introducing payment parity between in-person visits and virtual ones, the order expands access to care as current Massachusetts law allows insurers to limit coverage of telehealth services to insurer-approved health care providers in a telemedicine network.
The arrival of the pandemic and state of emergency has pushed for a rapid expansion of the use of technology in the practice of health care. Many of the barriers to access of health care via telemedicine have shifted in a relatively short period of time. In addition to Governor Baker’s order for payment parity, for example, the Governor allowed health care providers outside Massachusetts to obtain emergency licenses to practice within the Commonwealth. Before this and other similar licensure waivers, licensure requirements usually demand that providers be licensed within the state that their patients reside. By waiving this requirement, providers can expand the network of care they are able to provide, and telehealth serves to eliminate the only other barrier--distance.
 An additional movement towards lifting barriers to the implementation of telehealth services is the relaxation of Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) noncompliance enforcements by Health and Human Services, with the caveat that providers engage in good faith provision of telehealth during the national health emergency posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. HIPAA rules require the protection of privacy and security of health information. The discretionary enforcement order allows health care providers to use any non-public facing audio or video communication products during the COVID-19 public health emergency. This movement attempts to strike a balance between providing access to care during a national health emergency and the privacy protections against the risk of information exposure that are expected by patients in their interactions with their health care providers.
An additional movement towards lifting barriers to the implementation of telehealth services is the relaxation of Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) noncompliance enforcements by Health and Human Services, with the caveat that providers engage in good faith provision of telehealth during the national health emergency posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. HIPAA rules require the protection of privacy and security of health information. The discretionary enforcement order allows health care providers to use any non-public facing audio or video communication products during the COVID-19 public health emergency. This movement attempts to strike a balance between providing access to care during a national health emergency and the privacy protections against the risk of information exposure that are expected by patients in their interactions with their health care providers.
Another response to the public health crisis has been issued by the United States Drug Enforcement Agency, notifying that practitioners can, in light of the state of emergency, prescribe controlled substances in the absence of an in-person patient encounter. Prior, the prescription of controlled substances via telehealth evaluation was prohibited entirely. Now, prescribers are allowed to write prescriptions so long as: (1) the prescription is issued for a legitimate medical purpose in the course of the practitioner’s usual professional practice; (2) the telemedicine communication is conducted in a real-time, two-way, audio-visual communication system; and (3) the practitioner is acting in accordance to state and federal law.
As of May 2020, the Commonwealth of Massachusetts has initiated a four-phase reopening plan, beginning with hospitals and community health centers. The East Boston Neighborhood Health Center, for example, has indicated that they have an extensive screening process for patients who head over for in-person appointments, including the use of phone-tracking technology to notify staff when the patient has entered the building in an attempt to streamline entrance to examination rooms. The continued need to introduce methods of facilitating social distancing within the hospitals and community health centers indicates that there will be a continued incentive for the provision of telehealth services. The East Boston Neighborhood Health Center reports that, in the first phase of reopening, they expect 25% of visits to be in-person, with 75% of visits to continue to be via telehealth services such as video chat or over the phone.
While some find telehealth services to be inconvenient, due to technological challenges and care that requires more physical examination than can be completed over the phone or by video calling, it seems likely that we will see a blended version of care into the future. Health care practitioners have indicated that, while telemedicine is not a complete substitution of physically seeing and examining patients, being able to speak with a patient in combination with access to the patient’s medical history goes a long way in being able to diagnose and treat health problems. There is a growing sense of certainty that the use of a technology-based health care experience will “become the new normal.”
The natural question is how the legal landscape will have to adjust in response to the shift as society reopens and the balance of the role of technology in a “new normal” becomes more urgent to strike. Many of the barriers to the expansion of telehealth have been rapidly eliminated as a temporary alleviation in direct response to the public health crisis posed by COVID-19. This indicates that the changes are ephemeral; however, with the uncertainty posed by the length of the pandemic and the resulting impact this will have on the use of technology in health care, it seems likely that some of these legal shifts will need to be modified, rather than entirely eliminated, moving forward.
 Zahraa Badat anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
Zahraa Badat anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
United States v. Safehouse: Could Philadelphia be the First State in the Nation to Implement a Supervised Drug Injection Site?
The opioid epidemic is one of the worst public health crises affecting the United States, and the rate of deaths resulting from opioid overdose has steadily increased. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, a record high of more than 70,000 people died of a drug overdose in the United States in 2017, and over 47,000 of those deaths were from opioid overdoses. As lawmakers attempt to address this epidemic through public health initiatives , health advocates increasingly recommend using supervised injection sites to curb overdose deaths. Though legal barriers to this in the US exist, a recent District Court ruling in United States v. Safehouse may have paved the way for implementation of the first site of this kind in the US.
Injection sites provide a space where those using intravenous drugs can inject under the supervision of a medical professional ready to intervene in the event of an overdose, instead of unsupervised use where an overdose is more likely to be deadly. Supervised injection sites, also called safe injection facilities or safe consumption spaces, are a tertiary preventative public health measure aimed at combating overdose deaths and decreasing public use. In these spaces, injection drug users can self-administer drugs they bring to the facility in a controlled, sanitary environment under medical supervision. The medical personnel on staff at the sites do not directly handle the drugs and are there purely to administer Naloxone, an overdose reversal drug, in case of an overdose.
Despite the growing global presence in Europe, Australia, and Canada, scientific support for safe injection sites, and the interest of several cities, including Philadelphia, Boston, New York, Seattle, and San Francisco it is not entirely certain they can be operated in the United States. The Controlled Substances Act § 856, which regulates the production, possession, and distribution of controlled substances, makes it a criminal offense to maintain a drug-involved premises. Most academics agree that this “Crack House” Statute forbids safe injection sites and the courts can not definitively decide if safe injection site violate federal law until one is operational.
However, recently these assumptions have been called into question. Safe injection site proponents in many states have been appealing to legislatures and public health officials for funding. This effort has been largely unsuccessful due to political opposition and the looming threat of a federal lawsuit. In Philadelphia, which has the highest overdose rate of any major US city, a poll found roughly half of Philadelphians support a proposed safe injection site. Safehouse is a Philadelphia nonprofit that seeks to build the first safe injection site in the nation. In January 2018, Philadelphia health officials gave Safehouse permission to move forward with only private funds—preventing the need for legislative backing and appropriations.
In February 2019, federal prosecutors launched a civil lawsuit asking the U.S. District Court to rule on the legality of the Safehouse supervised consumption site plan, rather than waiting for the site to be built and then bringing federal criminal charges. U.S. Attorney William McSwain, working with Pennsylvania-based prosecutors, is seeking a declaratory judgment that medically supervised consumption sites per se violate 21 U.S.C § 856(a)(2)— the federal “Crack House” statute.
In February 2020, the court issued United States v. Safehouse, ruling that Safehouse’s plan to build a site where people could bring previously obtained drugs and use them under medical supervision for the purpose of combating fatal overdoses does not violate the Controlled Substances Act. Judge McHugh, looking at Congressional intent, ruled that §856 “does not prohibit Safehouse’s proposed medically supervised consumption rooms because Safehouse does not plan to operate them 'for the purpose of’ unlawful drug use within the meaning of the statute.” McHugh determines that at the time of enacting §856(a), Congress was focused on crack houses, not supervised drug injection sites. Even when amended in 2003, the focus was on “drug-fueled raves.” McHugh found that Congress neither expressly prohibited or authorized injection sites, so if §856(a) did not implicitly prohibit a consumption site, then implicit authorization naturally followed.
The question that the court addresses is whether the statute requires the defendant to know that third parties would enter their premises to consume illicit drugs, or rather that the defendant knowingly held their premises open for the purpose of facilitating illicit drug consumption. Judge McHugh concludes that the actor must “have acted for the proscribed purpose” to violate the statute. Therefore, the accused under a §856(a)(2) violation must have the purpose of facilitating illegal controlled substance use in the maintenance of a property.
Safehouse is planning “to make a place available for the purposes of reducing the harm of drug use, administering medical care, encouraging drug treatment, and connecting participants with social services.” The district court reasons that because of this, it could not conclude that Safehouse has, as a significant purpose, “the objective of facilitating drug use.”
In the wake of the ruling, U.S. Attorney McSwain announced that “this case is obviously far from over” and it is likely that the federal government will continue to litigate it. It is not unlikely that the Court that may hear this case on appeal disagrees with the District Court’s construction and strikes the legality of a supervised injection site based not on the intent of the person who controls the space, but the intent of the attendee of the site to use illicit drugs at that site, which has been the prevailing opinion up until the point of this ruling.
While the Safehouse case stands for an unexpected legal victory by way of the possibility of a supervised injection site to be opened in the United States, Philadelphia itself may not be the first state in the nation to implement one. The public sentiment in the wake of the decision was largely negative, with the local community being virulently opposed to the idea of a site being opened in the neighborhood from fear of what dangerous circumstances a site might attract. Plans to open the Safehouse site were put on indefinite hold. While proponents of Safehouse won the legal battle, winning over the community seems to be more of uphill battle than anticipated.
At this point in time, the legal position of supervised injection sites in the United States is tentatively positive. States who are looking to introduce this harm reduction initiative, and to be the first in the nation to do so, should take the opportunity to garner support from legislatures and local health care communities. While Philadelphia’s progression seems to be stymied, the District Court’s ruling provides significant legal precedent to ground encouragement for sites to be lobbied for in other states or cities that might not face the same type of community rejection that has prevented the opening of Safehouse.
 Zahraa Badat anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
Zahraa Badat anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
The Waiting Game: Supreme Court’s Decision on the Lawfulness of the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) Program
As May 2020 comes to an end, many eagerly await a Supreme Court decision that could affect the futures of thousands of DACA recipients and shape immigration policy as we know it. The Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) is the program that is currently under scrutiny; in particular the Supreme Court will be deciding on the following two issues: (1) “Whether or not the Trump administration’s decision to end DACA can be reviewed by the courts at all?” and (2) “Whether or not the Trump administration’s termination of DACA was lawful?” This program was first instituted under the Obama Administration as an executive action to do the following for qualified Dreamers who completed the process of a first-time or renewal application: (1) protection from deportation for a time period, and (2) work authorization for a set period of time.
During the Obama Administration, the DREAM Act of 2010 (H.R. 6497) was proposed and passed in the House but did not pass the Senate. The purpose, like its other variations, was intended to aid undocumented individuals by providing them a way to eventually reach legal status, because they were brought to the United States when they were children and have to live with a continued sense of uncertainty that attaches to being undocumented. In its stead, the Obama Administration designed a temporary solution, which came to be known as DACA, in which an individual could qualify by meeting a series of requirements (i.e. arriving in the United States before they turned sixteen years old).
This policy gave a lot of individuals hope, but everything changed with the arrival of the Trump Administration. The Trump Administration’s policies quickly took on an anti-immigration rhetoric, and his Administration rescinded the policy on the basis that it was illegal. Thereafter, lawsuits followed with Department of Homeland Security, et al., v. Regents of the University of California, et al. reaching the Supreme Court level.
Regarding the two issues laid out above, there are many ways the decision could go, but the one that would have the worst effect on DACA recipients would be the court siding on the Trump Administration’s side in saying that “DACA was an unconstitutional use of presidential power to begin with.” This could have a devastating impact on DACA recipients especially at a time when they find themselves in the midst of the COVID-19 global pandemic alongside the rest of the world.
For example, ABC News quotes a college student saying “As a DACA recipient, and everything going on with COVID-19 and as well with the Supreme Court ruling coming at any time -- It's been very stressful.” On top of college, she works with authorization under DACA, but COVID-19 has added other stressors as she finds herself as the only provider at home. Ending DACA at a time like this would end up being very challenging and harmful for individuals like these who are trying to stay afloat during this pandemic.
 Nevertheless, as this country struggles to recover from this pandemic, the most interesting development has happened to this Supreme Court case showing how vital Dreamers and immigrants have been to making this country function smoothly despite the havoc wreaked by the virus. A CNN report discusses how: “A letter sent to the Supreme Court states approximately 27,000 Dreamers are health care workers -- including 200 medical students, physician assistants, and doctors -- some of whom are now on the front lines in hospitals across the country.” The Supreme Court agreed to take this brief into consideration, and it makes one wonder whether the timing of the decision during a pandemic and the supplemental brief will have any impact at all?
Nevertheless, as this country struggles to recover from this pandemic, the most interesting development has happened to this Supreme Court case showing how vital Dreamers and immigrants have been to making this country function smoothly despite the havoc wreaked by the virus. A CNN report discusses how: “A letter sent to the Supreme Court states approximately 27,000 Dreamers are health care workers -- including 200 medical students, physician assistants, and doctors -- some of whom are now on the front lines in hospitals across the country.” The Supreme Court agreed to take this brief into consideration, and it makes one wonder whether the timing of the decision during a pandemic and the supplemental brief will have any impact at all?
Despite the positive contributions of these and other essential individuals, there have been a lot of issues that have also surfaced reflecting further difficulties that Dreamers are enduring. An example of this is federal funding under CARES Act. The pandemic has had even more disastrous effects on particular communities, and though the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act of 2020 was passed with a part of it designed to provide aid and federal dollars to help students, and yet the benefits are not available to everyone. DACA students could not qualify to receive money under this Act, and it was one of the reasons the Democrats reached out to Secretary DeVos to change the language but to no avail. The House has brought another bill to the forefront, the Heroes Act, which proposes many changes; one aspect of which directly seeks to overturn “Secretary DeVos’s decision to exclude DACA students from the emergency aid.”
This is a hopeful change, but the culmination of issues including the Supreme Court decision yet to be released, the uncertainty of COVID-19 on employment, health, and education, and a delay in passing the House bill paints a bleak picture.
Yet, at the end of the day, it is as Antonio Alarcon described it on CNN: “We’re hopeful that the Supreme Court will see the humanity of our stories and see the humanity of our families, because at the end of the day, this is a nation of immigrants.”
 Nabaa Khan anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.
Nabaa Khan anticipates graduating from Boston University School of Law in May 2021.