Drug-Free Treatment
4.1 Optoacoustic brain stimulation at submillimeter to single-neuron precision
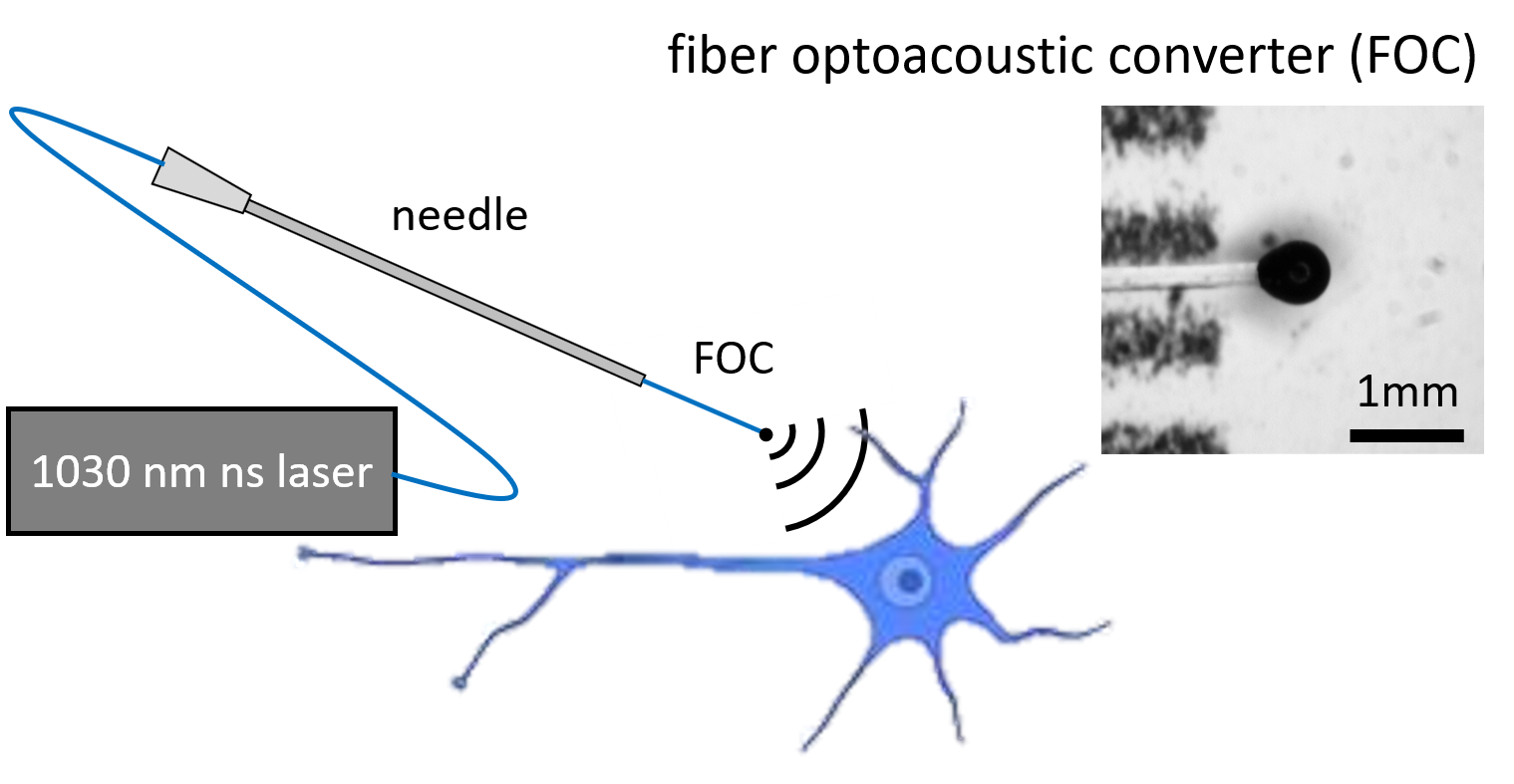
Low-intensity ultrasound is an emerging modality for neuromodulation. Yet, transcranial neuromodulation using low-frequency piezo-based transducers offers poor spatial confinement of excitation volume, often bigger than a few millimeters in diameter. In addition, the bulky size limits their implementation in a wearable setting and prevents integration with other experimental modalities. Here, we report spatially confined optoacoustic neural stimulation through a novel miniaturized Fiber-Optoacoustic Converter (FOC). The FOC has a diameter of 600 μm and generates an omnidirectional ultrasound wave locally at the fiber tip through the optoacoustic effect. We show that the optoacoustic wave can directly activate individual cultured neurons and generate intracellular Ca2+ transients. The FOC activates neurons within a radius of 500 μm around the fiber tip, delivering superior spatial resolution over conventional piezo-based low-frequency transducers. Using FOC, we demonstrated direct and spatially confined neural stimulation of mouse brain and modulation of motor activity in vivo. [Nature Communications 2020]