Publications
2024
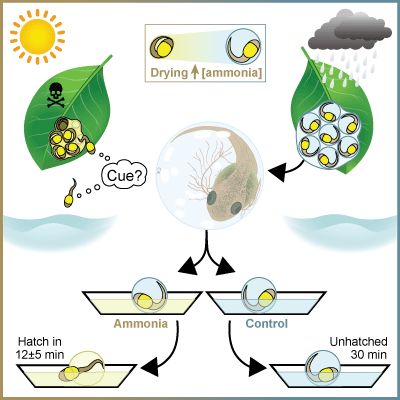 Lisondro-Arosemena A, Salazar-Nicholls MJ, Warkentin KM (2024) Elevated ammonia cues hatching in red-eyed treefrogs: A mechanism for escape from drying eggs. J Exp Zool B 342: 406–411. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.b.23253
Lisondro-Arosemena A, Salazar-Nicholls MJ, Warkentin KM (2024) Elevated ammonia cues hatching in red-eyed treefrogs: A mechanism for escape from drying eggs. J Exp Zool B 342: 406–411. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.b.23253
– Media coverage including STRI (in English & Spanish), La Prenza,

Güell BA, McDaniel JG, Warkentin KM (2024) Egg-clutch biomechanics affect escape-hatching behavior and performance. Integr Org Biol 6: obae006. https://doi.org/10.1093/iob/obae006
2023
Güell BA, Warkentin KM (2023) To hatch and hatch not: does heterochrony in onset of vestibular mechanosensing explain species differences in escape-hatching success of Agalychnis embryos in snake attacks? Behav Ecol Sociobiol 77: 141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-023-03417-4

Güell BA, Warkentin KM (2023) Phenology and environmental determinants of explosive breeding in gliding treefrogs: Diel timing of rainfall matters. Behav Ecol https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/arad072
Méndez-Narváez J, Warkentin KM (2023) Early onset of urea synthesis and ammonia detoxification pathways in three terrestrially developing frogs. J Comp Physiol B 193: 523–543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-023-01506-4
Gomez EK, Chaiyasarikul A, Güell BA, Warkentin KM (2023) Developmental changes in red-eyed treefrog embryo behavior increase escape-hatching success in wasp attacks. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 77: 52 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-023-03324-8
2022
Güell BA, Jung J, Almanzar A, Cuccaro-Díaz J, Warkentin KM (2022) Ontogeny of risk assessment and escape-hatching performance by red-eyed treefrog embryos in two threat contexts. J Exp Biol 225: jeb244533. DOI:10.1242/jeb.244533

Guevara-Molina EC, Ribeiro Gomes F, Warkentin KM (2022) Heat-induced hatching of red-eyed treefrog embryos: Hydration and clutch structure increase behavioral thermal tolerance. Integrative Organismal Biology obac041, DOI: 10.1093/iob/obac041
Majoris J, Francisco F, Burns C, Brandl S, Warkentin K, Buston P (2022) Paternal care regulates the timing, synchrony, and success of hatching in a coral reef fish. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 289: 20221466. DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2022.1466
Jung J, Guo M, Crovella ME, McDaniel JG, Warkentin KM (2022) Frog embryos use multiple levels of temporal pattern in risk assessment for vibration-cued hatching. Animal Cognition DOI: 10.1007/s10071-022-01634-4
Warkentin KM, Jung J, McDaniel JG (2022) Research approaches in mechanosensory-cued hatching and the iterative development of playback methods for red-eyed treefrog embryos. In Biotremology: Physiology, Ecology, and Evolution. Animal Signals and Communication, vol. 8. Eds. Hill PSM, Mazzoni V, Stritih Peljhan N, Virant-Doberlet M, Wessel A. Springer, Cham. p. 157–201. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-97419-0_7
Méndez-Narváez J, Warkentin KM (2022) Reproductive colonization of land by frogs: Embryos and larvae excrete urea to avoid ammonia toxicity. Ecology and Evolution DOI: 10.1002/ece3.8570
2021
Jung J, McDaniel JG, Warkentin KM (2021) Escape-hatching decisions show adaptive ontogenetic changes in how embryos manage ambiguity in predation risk cues. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 75: 141. DOI: 10.1007/s00265-021-03070-9
Warkentin KM (2021) Queering herpetology: On human perspectives and the study of diverse animals. Chapter 4 in Herpetologia Brasileira Contemporânea. Org. Toledo LF. Sociedade Brazileira de Herpetologia, São Paulo. p 42–58 [Proceedings of the IX Brazilian Herpetology Congress: Inclusive Herpetology.] pdf file of chapter
González K, Warkentin KM, Güell BA (2021) Dehydration-induced mortality and premature hatching in gliding treefrogs with even small reductions in humidity. Ichthyology & Herpetology 109: 21–30. DOI: 10.1643/h2020085
Gomez EK, Warkentin KM, Güell BA (2021) Egg-kicking behaviour by male gliding treefrogs (Agalychnis spurrelli Boulenger, 1913) does not dislodge competitors’ eggs. Herpetology Notes 14: 157–161
2020
Jung J, Serrano-Rojas SJ, Warkentin KM (2020) Multimodal mechanosensing enables treefrog embryos to escape egg predators Journal of Experimental Biology 223: jeb236141. DOI: 10.1242/jeb.236141

Delia J, Bravo-Valencia L, Warkentin KM (2020) The evolution of extended parental care in glassfrogs: Do egg-clutch phenotypes mediate coevolution between the sexes? Ecological Monographs 90: e01411. DOI 10.1002/ecm.1411
2019
Jung J, Kim SJ, Pérez Arias SM, McDaniel JG, Warkentin KM (2019) How do red-eyed treefrog embryos sense motion in predator attacks? Assessing the role of vestibular mechanoreception. Journal of Experimental Biology 222: jeb206052. DOI 10.1242/jeb.206052
Warkentin KM, Jung J, Rueda Solano LA, McDaniel JG (2019) Ontogeny of escape-hatching decisions: vibrational cue use changes as predicted from costs of sampling and false alarms. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 73: 51. doi: 10.1007/s00265-019-2663-2
Cohen KL, Piacentino M, Warkentin KM (2019) Two types of hatching gland cells facilitate escape-hatching at different developmental stages in red-eyed treefrogs, Agalychnis callidryas (Anura: Phyllomedusidae). Biol J Linn Soc doi: 10.1093/biolinnean/bly214
Delia J, Rivera JM, Salazar Nicholls MJ, Warkentin KM (2019) Hatching plasticity and the adaptive benefits of extended embryonic development in glassfrogs. Evol Ecol 33: 37–53. doi: 10.1007/s10682-018-9963-2
2018
Güell BA, Warkentin KM (2018) When and where to hatch? Red-eyed treefrog embryos use light cues in two contexts. PeerJ doi: 10.7717/peerj.6018
Hite JL, Hughey MC, Warkentin KM, Vonesh JR (2018) Cross-ecosystem effects of terrestrial predators link treefrogs, zooplankton, and aquatic primary production. Ecosphere 9: e02377. doi: 10.1002/ecs2.2377
Cohen, KL, Piacentino ML, Warkentin KM. (2018) The hatching process and mechanisms of adaptive hatching acceleration in hourglass treefrogs. J Comp Biochem Physiol A. 217: 63–74 doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.10.020
2017
Salica MJ, Vonesh JR, Warkentin KM. (2017) Egg clutch dehydration induces early hatching in red-eyed treefrogs, Agalychnis callidryas. PeerJ. 5:e3549. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3549
Warkentin KM, Cuccaro Diaz J, Güell BA, Jung J, Kim SJ, Cohen KL. (2017) Developmental onset of escape-hatching responses in red-eyed treefrogs depends on cue type. Anim Behav. 129: 103–112. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2017.05.008
 Delia J, Bravo-Valencia L, Warkentin KM. (2017) Patterns of parental care in Neotropical glassfrogs: fieldwork alters hypotheses of sex-role evolution. J Evol Biol. doi: 10.1111/jeb.13059
Delia J, Bravo-Valencia L, Warkentin KM. (2017) Patterns of parental care in Neotropical glassfrogs: fieldwork alters hypotheses of sex-role evolution. J Evol Biol. doi: 10.1111/jeb.13059
2016
Rueda Solano LA, Warkentin KM. (2016) Foraging behavior with possible use of substrate-borne vibrational cues for prey localization in Atelopus laetissimus (Ruiz-Carranza, Ardila-Robayo, and Hernández-Camacho, 1994). Herp Notes. 9: 191–195.

Cohen KL, Seid MA, Warkentin KM. (2016) How embryos escape from danger: the mechanism of rapid, plastic hatching in red-eyed treefrogs. J Exp Biol 219: 1875-1883. doi: 10.1242/jeb.139519
Bouchard SS, O’Leary CJ, Wargelin LJ, Charbonnier JF, Warkentin KM (2016) Post-metamorphic carryover effects of larval digestive plasticity. Funct Ecol 30: 379–388 doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12501
2015
Bouchard SS, O’Leary CJ, Wargelin LJ, Rodriguez WB, Jennings KX, Warkentin KM (2015) Alternative competition-induced digestive strategies yield equal growth but constrain compensatory growth in red-eyed treefrog larvae. J Exp Zool 323A: 778–788. doi: 10.1002/jez.1991
McCoy MW, Wheat SK, Warkentin KM, Vonesh JR (2015) Risk assessment based on indirect predation cues: Revisiting fine-grained variation. Ecol Evol doi: 10.1002/ece3.1552
Hughey MC, Rogge JR, Thomas K, McCoy MW, Warkentin KM (2015) Escape-hatching responses of individual treefrog embryos vary with threat level in wasp attacks: a mechanistic analysis. Behaviour doi:10.1163/1568539X-00003291
Touchon JC, McCoy MW, Landberg T, Vonesh JR, Warkentin KM (2015) Putting µ/g in a new light: plasticity in life-history switch points reflects fine-scale adaptive responses. Ecology 96: 2192–2202.
 Tarvin RD, Silva Bermúdez C, Briggs VS, Warkentin KM (2015) Carry-over effects of size at metamorphosis in red-eyed treefrogs: higher survival but slower growth of larger metamorphs. Biotropica 47:218–226.
Tarvin RD, Silva Bermúdez C, Briggs VS, Warkentin KM (2015) Carry-over effects of size at metamorphosis in red-eyed treefrogs: higher survival but slower growth of larger metamorphs. Biotropica 47:218–226.
2014
Willink B, Palmer MS, Landberg T, Vonesh JR , Warkentin KM (2014) Environmental context shapes immediate and cumulative costs of risk-induced early hatching. Evol Ecol 28:103-116
2013
 Touchon JC, Jiménez RR, Abinette SH, Vonesh JR, Warkentin KM (2013) Behavioral plasticity mitigates risk across environments and predators during anuran metamorphosis. Oecologia 173:801-811
Touchon JC, Jiménez RR, Abinette SH, Vonesh JR, Warkentin KM (2013) Behavioral plasticity mitigates risk across environments and predators during anuran metamorphosis. Oecologia 173:801-811
Gomez-Mestre I, Warkentin KM (2013) Risk-induced hatching timing shows low heritability and evolves independently of spontaneous hatching in red-eyed treefrogs. J Evol Biol 26:1079-1089
Touchon JC, McCoy MW, Vonesh JR, Warkentin KM (2013) Effects of plastic hatching timing carry over through metamorphosis in red-eyed treefrogs. Ecology 94:850-860
2012
Hughey MC, McCoy MW, Vonesh JR, Warkentin KM (2012) Spatial contagion shapes colonization dynamics of frogflies (Megaselia sp. nov.) on clutches of red-eyed treefrogs (Agalychnis callidryas). Biol Lett 8:887-889
Hughey MC, Nicolás A, Vonesh JR, Warkentin KM (2012) Wasp predation drives the assembly of fungal and fly communities on frog egg masses. Oecologia 168:1057-1068
McCoy MW, Touchon JC, Landberg T, Warkentin KM, Vonesh JR (2012) Prey responses to predator chemical cues: disentangling the importance of the number and biomass of prey consumed by predators. PLoS ONE 7:e47495
Wibowo E, Wassersug R, Warkentin K, Walker L, Robinson J, Brotto L, Johnson T (2012) Impact of androgen deprivation therapy on sexual function: A response. Asian J Andrology 14:793-794 doi:10.1038/aja.2012.60
2011
Gonzalez S, Touchon JC, Vonesh JR (2011) Interactions between competition and predation shape early growth and survival of two Neotropical hylid tadpoles. Biotropica 43:633-639
McCoy MW, Bolker BM, Warkentin KM, Vonesh JR (2011) Predicting predation through prey ontogeny using size-dependent functional response models. Am Nat 177:752-766
Touchon JC, Urbina J, Warkentin KM (2011) Habitat-specific constraints on induced hatching in a treefrog with reproductive mode plasticity. Behav Ecol 22:169-175
Touchon JC, Warkentin KM (2011) Thermally contingent plasticity: temperature alters expression of predator-induced color and morphology in a Neotropical treefrog tadpole. J Anim Ecol 80:79-88
 Warkentin KM (2011) Environmentally cued hatching across taxa: Embryos respond to risk and opportunity. Integr Comp Biol 51:14-25
Warkentin KM (2011) Environmentally cued hatching across taxa: Embryos respond to risk and opportunity. Integr Comp Biol 51:14-25
Warkentin KM (2011) Plasticity of hatching in amphibians: Evolution, trade-offs, cues and mechanisms. Integr Comp Biol 51:111-127
2010
 Caldwell MS, Johnston GR, McDaniel JG, Warkentin KM (2010) Vibrational signaling in the agonistic interactions of red-eyed treefrogs. Curr Biol 20:1012-1017
Caldwell MS, Johnston GR, McDaniel JG, Warkentin KM (2010) Vibrational signaling in the agonistic interactions of red-eyed treefrogs. Curr Biol 20:1012-1017
Caldwell MS, McDaniel JG, Warkentin KM (2010) Is it safe? Red-eyed treefrog embryos assessing predation risk use two features of rain vibrations to avoid false alarms. Anim Behav 79:255-260
 Gomez-Mestre I, Saccocio VL, Iijima T, Collins EM, Rosenthal GG, Warkentin KM (2010) The shape of things to come: linking developmental plasticity to post-metamorphic morphology in anurans. J Evol Biol 23:1364-1373
Gomez-Mestre I, Saccocio VL, Iijima T, Collins EM, Rosenthal GG, Warkentin KM (2010) The shape of things to come: linking developmental plasticity to post-metamorphic morphology in anurans. J Evol Biol 23:1364-1373
Touchon JC, Warkentin KM (2010) Short- and long-term effects of the abiotic egg environment on viability, development and vulnerability to predators of a Neotropical anuran. Funct Ecol 24:566-575
2009
Caldwell MS, McDaniel JG, Warkentin KM (2009) Frequency information in the vibration-cued escape hatching of red-eyed treefrogs. J Exp Biol 212:566-575
Touchon JC, Warkentin KM (2009) Negative synergism of rainfall patterns and predators affects frog egg survival. J Anim Ecol 78:715-723
Warkentin KM, Caldwell MS (2009) Assessing risk: embryos, information, and escape hatching. In: Dukas R, Ratcliffe JM (eds) Cognitive ecology II. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 177-200
2008
Gomez-Mestre I, Touchon JC, Saccocio VL, Warkentin KM (2008) Genetic variation in pathogen-induced early hatching of toad embryos. J Evol Biol 21:791-800
Gomez-Mestre I, Wiens JJ, Warkentin KM (2008) Evolution of adaptive plasticity: risk-sensitive hatching in neotropical leaf-breeding treefrogs. Ecol Monogr 78:205-224
 Rogge JR, Warkentin KM (2008) External gills and adaptive embryo behavior facilitate synchronous development and hatching plasticity under respiratory constraint. J Exp Biol 211:3627-3635
Rogge JR, Warkentin KM (2008) External gills and adaptive embryo behavior facilitate synchronous development and hatching plasticity under respiratory constraint. J Exp Biol 211:3627-3635
 Touchon JC, Warkentin KM (2008) Reproductive mode plasticity: Aquatic and terrestrial oviposition in a treefrog. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:7495-7499
Touchon JC, Warkentin KM (2008) Reproductive mode plasticity: Aquatic and terrestrial oviposition in a treefrog. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:7495-7499
Touchon JC, Warkentin KM (2008) Fish and dragonfly nymph predators induce opposite shifts in color and morphology of tadpoles. Oikos 117: 634-640.
2007
Gomez-Mestre I, Warkentin KM (2007) To hatch and hatch not: similar selective trade-offs but different responses to egg predators in two closely related, syntopic treefrogs. Oecologia 153:197-206
Warkentin KM (2007) Oxygen, gills, and embryo behavior: mechanisms of adaptive plasticity in hatching. Comp Biochem Phys A 148:720-731
Warkentin KM, Caldwell MS, Siok TD, D’Amato AT, McDaniel JG (2007) Flexible information sampling in vibrational assessment of predation risk by red-eyed treefrog embryos. J Exp Biol 210:614-619 [Inside JEB commentary]
2006
 Gomez-Mestre I, Touchon JC, Warkentin KM (2006) Amphibian embryo and parental defenses and a larval predator reduce egg mortality from water mold. Ecology 87:2570-2581
Gomez-Mestre I, Touchon JC, Warkentin KM (2006) Amphibian embryo and parental defenses and a larval predator reduce egg mortality from water mold. Ecology 87:2570-2581
Touchon JC, Gomez-Mestre I, Warkentin KM (2006) Hatching plasticity in two temperate anurans: responses to a pathogen and predation cues. Can J Zool 84:556-563
 Vonesh JR, Warkentin KM (2006) Opposite shifts in size at metamorphosis in response to larval and metamorph predators. Ecology 87:556-562
Vonesh JR, Warkentin KM (2006) Opposite shifts in size at metamorphosis in response to larval and metamorph predators. Ecology 87:556-562
Warkentin KM, Buckley CR, Metcalf KA (2006) Development of red-eyed treefrog eggs affects efficiency and choices of egg-foraging wasps. Anim Behav 71:417-425
Warkentin KM, Caldwell MS, McDaniel JG (2006) Temporal pattern cues in vibrational risk assessment by red-eyed treefrog embryos, Agalychnis callidryas. J Exp Biol 209:1376-1384 [Inside JEB commentary]
Warkentin KM, Gray RE, Wassersug RJ (2006) Restoration of satisfying sex for a castrated cancer patient with complete impotence: a case study. J Sex Marital Ther 32:389-399
2005
Warkentin KM (2005) How do embryos assess risk? Vibrational cues in predator-induced hatching of red-eyed treefrogs. Anim Behav 70:59-71
Warkentin KM, Gomez-Mestre I, McDaniel JG (2005) Development, surface exposure, and embryo behavior affect oxygen levels in eggs of the red-eyed treefrog, Agalychnis callidryas. Physiol Biochem Zool 78:956-966
Earlier
Warkentin KM (2002) Hatching timing, oxygen availability, and external gill regression in the tree frog, Agalychnis callidryas. Physiol Biochem Zool 75:155-164
Warkentin KM, Currie CC, Rehner SA (2001) Egg-killing fungus induces early hatching of red-eyed treefrog eggs. Ecology 82:2860-2869
Warkentin KM, Wassersug RJ (2001) Do prostaglandins regulate external gill regression in anurans? J Exp Zool 289:366-373
Warkentin KM (2000) Wasp predation and wasp-induced hatching of red-eyed treefrog eggs. Anim Behav 60:503-510
Warkentin KM (2000) Environmental and developmental effects on external gill loss in the red-eyed treefrog, Agalychnis callidryas. Physiol Biochem Zool 73:557-565
Warkentin KM (1999) The development of behavioral defenses: a mechanistic analysis of vulnerability in red-eyed tree frog hatchlings. Behav Ecol 10:251-262
Warkentin KM (1999) Effects of hatching age on development and hatchling morphology in the red-eyed treefrog, Agalychnis callidryas. Biol J Linn Soc 68:443-470
Warkentin KM (1995) Adaptive plasticity in hatching age: a response to predation risk trade-offs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:3507-3510
Ryan MJ, Warkentin KM, McClelland BE, Wilczynski W (1995) Fluctuating asymmetries and advertisement call variation in the cricket frog, Acris crepitans. Behav Ecol 6:124-131
Warkentin KM (1992) Microhabitat use and feeding rate variation in green frog tadpoles (Rana clamitans). Copeia 1992:731-740
Warkentin KM (1992) Effects of temperature and illumination on feeding rates of green frog tadpoles (Rana clamitans). Copeia 1992:725-730
