 Adaptive ultrasound beamforming Adaptive ultrasound beamforming
Improved ultrasound images are obtained by suppression of incoherent clutter and noise. Read more… |
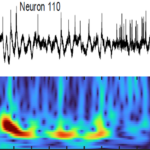 High contrast voltage imaging High contrast voltage imaging
Genetically encoded voltage indicators (GEVIs) are imaged at kilohertz rates by targeted-illumination and confocal microscopy. Read more… |
 Deblurring by pixel reassignment Deblurring by pixel reassignment
General algorithm for image sharpening is based on pixel reassignment. Read more… |
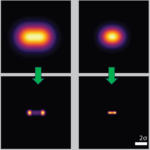
 Imaging at trillion frames per second Imaging at trillion frames per second
Single-shot non-synchronous array photography (SNAP) is performed with time-to-angle multiplexing. Read more… |
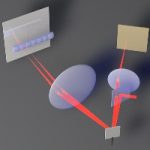 Ultrafast laser scanning Ultrafast laser scanning
A passive scan multiplier unit enables a galvanometer to perform high throughput ultrafast laser scanning beyond the inertia limit. Read more… |
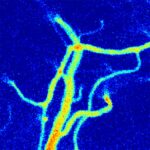 Laser speckle contrast imaging Laser speckle contrast imaging
Multifocus laser speckle contrast imaging (LSCI) reveals mixed blood-flow dynamics in the brain. Read more… |
 Ultrasound phase-contrast imaging Ultrasound phase-contrast imaging
Differential phase contrast using the memory effect enables a standard US imaging device to reveal subsurface speed-of-sound variations in real time. Read more… |
 Widefield multifocus imaging Widefield multifocus imaging
High-contrast multifocus microscopy is performed with a single camera and versatile z-splitter prism. Read more… |
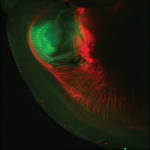
 Retroillumination corneal imaging Retroillumination corneal imaging
Widefield corneal imaging is performed by oblique retroillumination microscopy. Read more… |
 Reverberation multiphoton microscopy Reverberation multiphoton microscopy
Quasi-simultaneous multiplane imaging is performed using temporal multiplexing with a reverberation loop. Read more… |
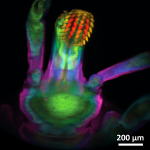 Multi-Z confocal microscopy Multi-Z confocal microscopy
Simultaneous multiplane imaging is performed over large fields of view at rates up to a kilohertz. Read more… |
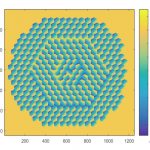 Compressive flow cytometry Compressive flow cytometry
High-throughput flow cytometry is performed with matched-filter compressive imaging. Read more… |
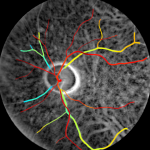 Transcranial retinal imaging Transcranial retinal imaging
Transcranial retinal imaging is a method for transilluminating the ocular fundus (i.e. the back of the eye). Read more…
|
 Extended-depth-of-field microscopy Extended-depth-of-field microscopy
Computational and physical variations of extended-depth-of-field (EDOF) imaging lead to increased contrast. Read more…
|
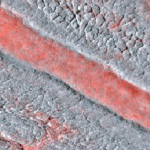 Oblique back-illumination microscopy Oblique back-illumination microscopy
OBM provides DIC-like phase contrast in arbitrarily thick tissue. The technique is simple, fast, and can be implemented in camera- or scanning-based configurations. Read more… |
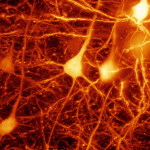 Active illumination microscopy Active illumination microscopy
AIM significantly increases the dynamic range and enhances the weak-signal sensitivity of a scanning fluorescence microscope, without loss of information. Read more… |
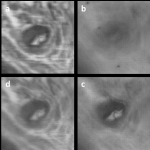 Imaging through complex media Imaging through complex media
Variants of adaptive optics are used to improve imaging through an aberrating screen or to control spectral decorrelation through a scattering medium. Read more… |
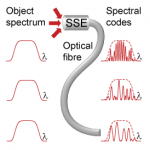 Imaging through a single optical fiber Imaging through a single optical fiber
Self-luminous objects are imaged through a single optical fiber using spread-spectral encoding. The method contains no moving parts and is insensitive to fiber bending. Read more… |
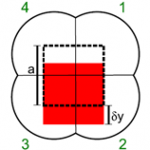 Partitioned aperture wavefront imaging Partitioned aperture wavefront imaging
Single-shot, quantitative phase imaging using a specially constructed lens. Our technique is achromatic, polarization independent, and light-efficient. Read more… |
 HiLo microscopy HiLo microscopy
HiLo microscopy enables a standard widefield fluorescence or reflectance microscope to provide optical sectioning by using two images acquired with uniform and non-uniform (or “structured”) illumination. Read more… |
 Differential aberration imaging Differential aberration imaging
DAI enables multiphoton contrast enhancement by near-instantaneously acquiring non-aberrated and aberrated images. Read more… |
 Dynamic speckle illumination microscopy Dynamic speckle illumination microscopy
DSI microscopy enables a standard widefield fluorescence microscope to provide optical sectioning by using randomly changing speckle illumination. Read more… |
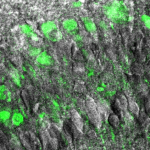 Autoconfocal microscopy Autoconfocal microscopy
Autoconfocal microscopy (ACM) enables a two-photon excited fluorescence microscope to produce simultaneous phase contrast by using a virtual pinhole in the transmission direction. Read more… |
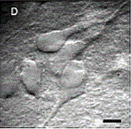 Graded field microscopy Graded field microscopy
Graded field microscopy reveals phase gradients in a sample by combining oblique illumination with oblique detection. The resulting image resembles DIC. Read more… |
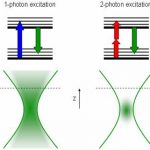 Nonlinear microscopy Nonlinear microscopy
Nonlinear optical microscopy provides contrast based on a nonlinear interaction of light and matter. Examples include two-photon excited fluorescence (TPEF) and second harmonic generation (SHG) microscopy. Read more… |