Projects
This page contains brief descriptions of several HEECMA-related projects. Please follow the links below for more details.
- Optimized Cuckoo Filter: Membership testing has many networking applications like distributed caching, peer-to-peer networks, or resource routing, to name a few. Several studies have reported the advantages of using membership testing in Software Defined Networking, and Bloom Filters have been widely adopted for that purpose. Cuckoo Filters is a recently proposed alternative to Bloom that outperforms them in terms of speed and memory efficiency, with some drawbacks. We propose an Optimized Cuckoo Filter (OCF) design that limits some of the Cuckoo Filter drawbacks and gives a better-amortized search time, with fewer false positives. [more details]
- COSE: The cost of cloud usage and performance of a serverless application is
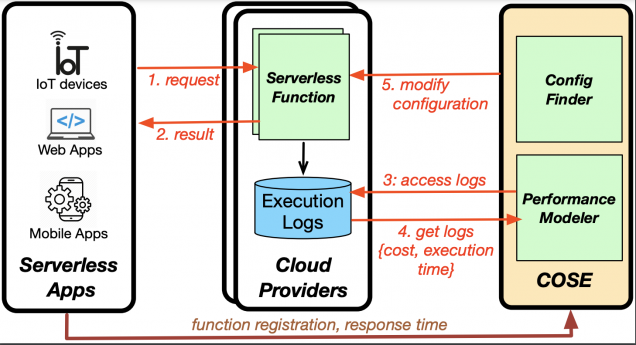 affected by various configurable parameters of serverless functions such as memory, CPU, and location. To address the challenge of configuring these parameters optimally, we built COSE. It is a framework that uses Bayesian Optimization to find the optimal configuration for serverless functions. It uses statistical learning techniques to intelligently collect samples and predict the cost and execution time of a serverless function across unseen configuration values. We evaluated COSE not only on a commercial cloud provider, where we successfully found optimal/near-optimal configurations in as few as five samples but also over a wide range of simulated distributed cloud environments that confirm the efficacy of our approach. [Video][more details]
affected by various configurable parameters of serverless functions such as memory, CPU, and location. To address the challenge of configuring these parameters optimally, we built COSE. It is a framework that uses Bayesian Optimization to find the optimal configuration for serverless functions. It uses statistical learning techniques to intelligently collect samples and predict the cost and execution time of a serverless function across unseen configuration values. We evaluated COSE not only on a commercial cloud provider, where we successfully found optimal/near-optimal configurations in as few as five samples but also over a wide range of simulated distributed cloud environments that confirm the efficacy of our approach. [Video][more details] - LIBRA: LIBRA is a balanced (hybrid) approach that leverages both VM-based and serverless resources to efficiently manage cloud resources for the applications. LIBRA closely monitors the application demand and provisions appropriate VM and serverless resources such that the running cost is minimized, and Service-Level Agreements are met. Unlike state-of-the-art, LIBRA not only hides VM cold-start delays, and hence reduces response time, by leveraging serverless, but also directs a low-rate bursty portion of the demand to serverless where it would be less costly than spinning up new VMs. We evaluated LIBRA on real traces in a simulated environment as well as on the AWS commercial cloud. Our results show that LIBRA outperforms other resource-provisioning policies, including a recent hybrid approach – LIBRA achieves more than 85% reduction in SLA violations and up to 53% in cost savings. [more details]
- Federated Split Learning: To better preserve user and data privacy and at the same time guarantee high performance, distributed machine learning techniques such as Federated and Split Learning have been recently proposed. Both of these distributed learning architectures have merits but also drawbacks. In this work, we analyze such tradeoffs and propose a new hybrid Federated Split Learning architecture, to combine the benefits of both in terms of efficiency and privacy. Our evaluation shows how Federated Split Learning may reduce the computational power required for each client running a Federated Learning and enable Split Learning parallelization while maintaining a high prediction accuracy with unbalanced datasets during training. Furthermore, FSL provides a better accuracy-privacy tradeoff in specific privacy approaches compared to Parallel Split Learning. [more details]