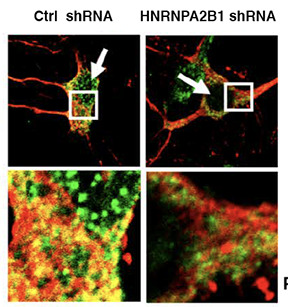
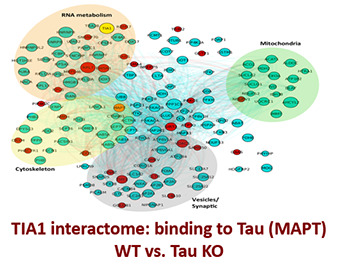
Novel Concepts
Phase Separation and the Biophysics of Membraneless Organelles
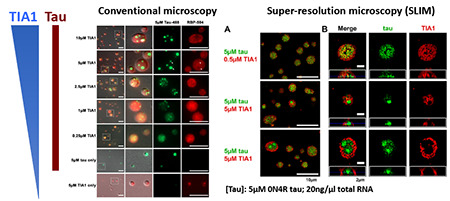
Many proteins can self-associate through multiple weak interactions. This allows functionally linked proteins to associate in molecular condensates termed “Membraneless Organelles” (MOs). MOs include the nucleolus, stress granules and many nuclear bodies. The biophysics of the process is fascinating because these weak interactions allow the proteins to coalesce into dynamic structures that behave exactly like lipids, fusing into big droplets or being broken into little droplets just like oil in vinegar. RNA is an essential substrate that promotes phase separation and formation of MOs. Our recent publication in PNAS presents two important discoveries: 1) that tau preferentially partitions into droplets containing TIA1 and 2) that the secondary structure of RNA regulates tau phase separation.
Ash, P. E. A., Lei, S., …… Wolozin. B., TIA1 potentiates tau phase separation and promotes generation of toxic oligomeric tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021, 118(9):e2014188118. PMID: 33619090.
Wolozin, B., Ivanov, P., Stress granules and neurodegeneration. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2019. 20(11): 649-66. PMCID: PMC6986315doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0222-5.
RNA binding proteins and disease
Genetic studies show a striking number of genetic linkages to neurodegenerative diseases in the family of proteins termed RNA binding proteins (RBPs). Why? Work in our laboratory has focused on sorting out this question. RBPs function by phase separating together to form membraneless organelles, such as stress granules, translational complexes, the nucleolus, nuclear pores, etc. Many of the disease-linked RBPs fall into the class of stress granule proteins, and these proteins exhibit a strong tendency to irreversibly aggregate. For some RBPs, such as TDP-43 and FUS, aggregation might impair key functions, such as RNA splicing. The mechanism by which other RBPs contribute to disease, such as TIA1, is unclear. Our publications have presented multiple discoveries including, 1) that TDP-43 forms stress granules and associates with stress granules in pathological tissue, 2) that TIA1 forms the crucible for tau oligomers and regulates tau-mediated neurodegeneration, and 3) that tau selectively binds to RNA containing N6-methyladenosine (m6A).
Lulu Jiang, Weiwei Lin, ……Andrew Emili, Benjamin Wolozin, A Complex Containing HNRNPA2B1 and N6-methyladenosine Modified Transcripts Mediates Actions of Toxic Tau Oligomers. (BIORXIV/2020/409334)
Pourhaghighi, R, Ash, PEA, ……. Wolozin, B, and Emili, A, BraInMap elucidates the macromolecular connectivity landscape of mammalian brain. Cell Syst. 2020 Apr 22;10(4):333-350.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2020.03.003. PMID: 32325033
Vanderweyde, T., Apicco, D.J., Youmans-Kidder, K., Ash, P.E.A., Cook, C., da Rocha, E.L., Jansen-West, K., Frame, A.A., Citro, A., Ivanov, P., Abisambra, J.F., Steffen, M., Li, H., Petrucelli, L., Wolozin, B., Interaction with tau with RNA binding protein TIA1 regulates tau pathophysiology and toxicity. Cell Reports 15: 1-12 (2016). PMID: 27160897
Pathophysiology of Tau in AD/FTD: epi-Transcriptomics
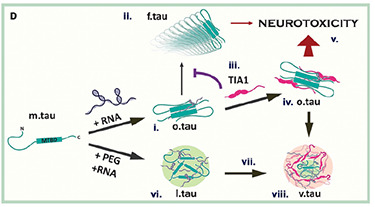
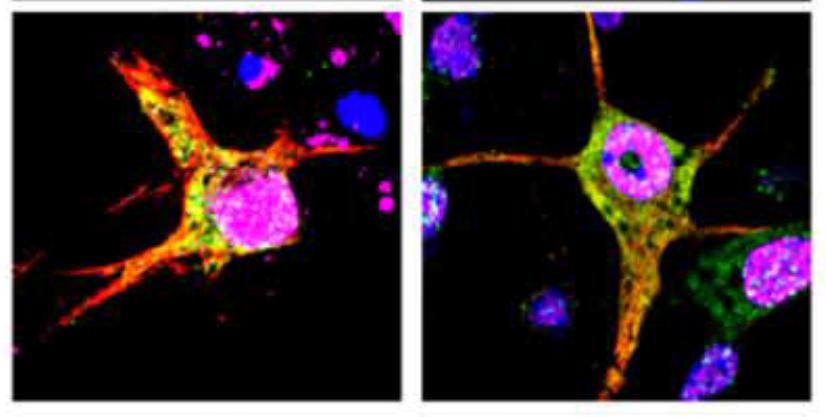
Why would the body set up a system that allows tau aggregation? We hypothesize that phosphorylation and subsequent oligomerization of tau (oTau) represents a normal biological function of tau. Our data suggests that oTau selectively partitions into TIA1 stress granules, where it is stabilized and functions to promote the translational stress response, which means that it helps to adapt protein synthesis to stress. Our recent manuscript (Jiang, et al, BioRx) shows that oTau selectively associates with RNA methylated on adenosines at the N6 position (m6A) through binding to the ALS-linked RBP, HNRNPA2B1. This complex reduces protein synthesis during stress. However, persistent stress leads to toxic accumulation of oTau and neurodegeneration. Our publications have presented multiple discoveries about this system, including: 1) oTau pathology co-localizes with TIA1, HNRNPA2B1 and other RPBs in as part of the pathology of tauopathies, 2) TIA1 and HNRNPA2B1 are required for tau mediated neurodegeneration, 3) TIA1 and oTau associate with many other disease linked RBPs.
m6A and Alzheimer pathology
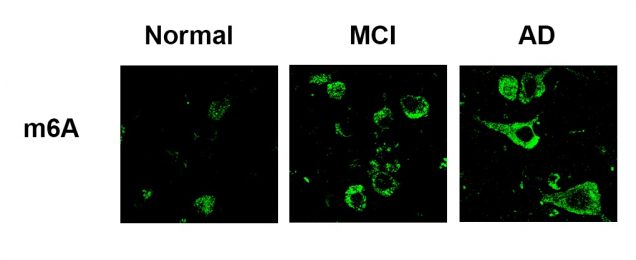
The m6A story continues to grow stronger. We find that levels of m6A show a striking 4-fold increase with disease progression among AD subjects, levels of the m6A::oTau complex increase over 6-fold with disease progression. These same disease-dependent changes are evident in P301S tau mice. The complex is essential for disease progression because knockdown of HNRNPA2B1 or METTL3 (the methyltransferase that adds m6A) breaks up the complex, reduces tau pathology and reduces neurodegeneration. We are currently examining the RNA species that are methylated to determine which types of RNA and which transcripts of mRNA contain m6A, and how these change with disease.
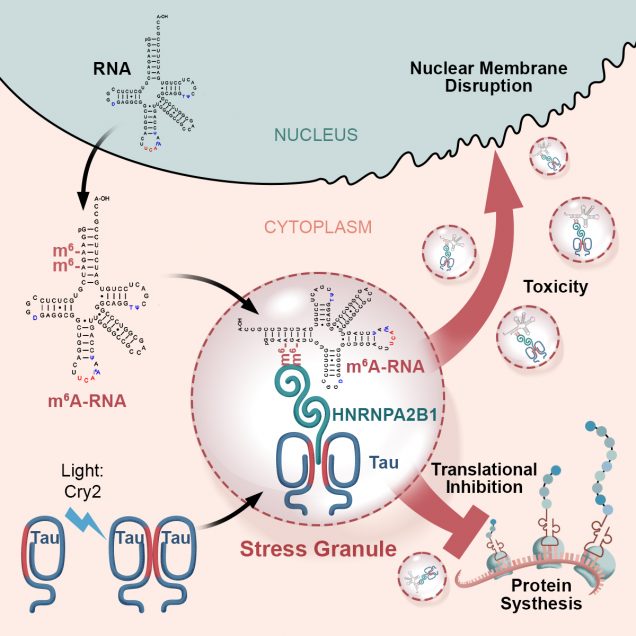
Lulu Jiang, Weiwei Lin, ……Andrew Emili, Benjamin Wolozin, A Complex Containing HNRNPA2B1 and N6-methyladenosine Modified Transcripts Mediates Actions of Toxic Tau Oligomers. (BIORXIV/2020/409334) Jiang, L., Ash, P. E. A., Maziuk, B. F., Balance, S., Boudeau, Abdullatif, A. A., Orlando, M., Petrucelli, L., Ikezu, T., Wolozin, B., TIA1 regulates the generation and response to toxic tau oligomers. Acta Neuropathologica Scandinavia. 2019, 137(2):259-77. PMID 30465259. doi.org/10.1007/s00401-018-1937-5.
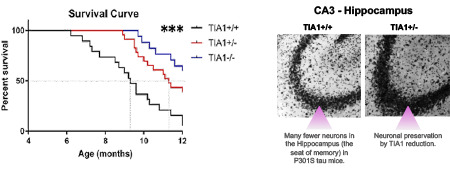
Apicco, D.J., Ash, P.E.A., ……..Wolozin, B., Reducing TIA1 protects against tau-mediated neurodegeneration in vivo. Nature Neuroscience, 2018 21(1):72-80. PMC5745051
Vanderweyde, T., Apicco, D.J., Youmans-Kidder, K., Ash, P.E.A., Cook, C., da Rocha, E.L., Jansen-West, K., Frame, A.A., Citro, A., Ivanov, P., Abisambra, J.F., Steffen, M., Li, H., Petrucelli, L., Wolozin, B., Interaction with tau with RNA binding protein TIA1 regulates tau pathophysiology and toxicity. Cell Reports 15: 1-12 (2016). PMID: 27160897
Vanderweyde, T., Yu, H., Varnum, M., Liu-Yesucevitz, L., Citro, A., Ikezu, T., Duff, K., Wolozin, B., Contrasting Pathology of Stress Granule Proteins TIA-1 and G3BP in Tauopathies. J. Neurosci. 32:8270-83 (2012). PMID: 22699908
Pathophysiology of Tau in AD/FTD
Why would the body set up a system that allows tau aggregation? We hypothesize that phosphorylation and subsequent oligomerization of tau (oTau) represents a normal biological function of tau. Our data suggests that oTau selectively partitions into TIA1 stress granules, where it is stabilized and functions to promote the translational stress response, which means that it helps to adapt protein synthesis to stress. Our recent manuscript (Jiang, et al, BioRx) shows that oTau selectively associates with m6A RNA probably through binding to the ALS-linked RBP, HNRNPA2B1. This complex reduces protein synthesis during stress. However, persistent stress leads to toxic accumulation of oTau and neurodegeneration. Our publication have presented multiple discoveries about this system, including: 1) oTau pathology co-localizes with TIA1, HNRNPA2B1 and other RPBs in as part of the pathology of tauopathies, 2) TIA1 and HNRNPA2B1 are required for tau mediated neurodegeneration, 3) TIA1 and oTau associate with many other disease linked RBPs.
Lulu Jiang, Weiwei Lin, ……Andrew Emili, Benjamin Wolozin, A Complex Containing HNRNPA2B1 and N6-methyladenosine Modified Transcripts Mediates Actions of Toxic Tau Oligomers. (BIORXIV/2020/409334)
Jiang, L., Ash, P. E. A., Maziuk, B. F., Balance, S., Boudeau, Abdullatif, A. A., Orlando, M., Petrucelli, L., Ikezu, T., Wolozin, B., TIA1 regulates the generation and response to toxic tau oligomers. Acta Neuropathologica Scandinavia. 2019, 137(2):259-77. PMID 30465259. doi.org/10.1007/s00401-018-1937-5.
Apicco, D.J., Ash, P.E.A., ……..Wolozin, B., Reducing TIA1 protects against tau-mediated neurodegeneration in vivo. Nature Neuroscience, 2018 21(1):72-80. PMC5745051
Vanderweyde, T., Apicco, D.J., Youmans-Kidder, K., Ash, P.E.A., Cook, C., da Rocha, E.L., Jansen-West, K., Frame, A.A., Citro, A., Ivanov, P., Abisambra, J.F., Steffen, M., Li, H., Petrucelli, L., Wolozin, B., Interaction with tau with RNA binding protein TIA1 regulates tau pathophysiology and toxicity. Cell Reports 15: 1-12 (2016). PMID: 27160897
Vanderweyde, T., Yu, H., Varnum, M., Liu-Yesucevitz, L., Citro, A., Ikezu, T., Duff, K., Wolozin, B., Contrasting Pathology of Stress Granule Proteins TIA-1 and G3BP in Tauopathies. J. Neurosci. 32:8270-83 (2012). PMID: 22699908