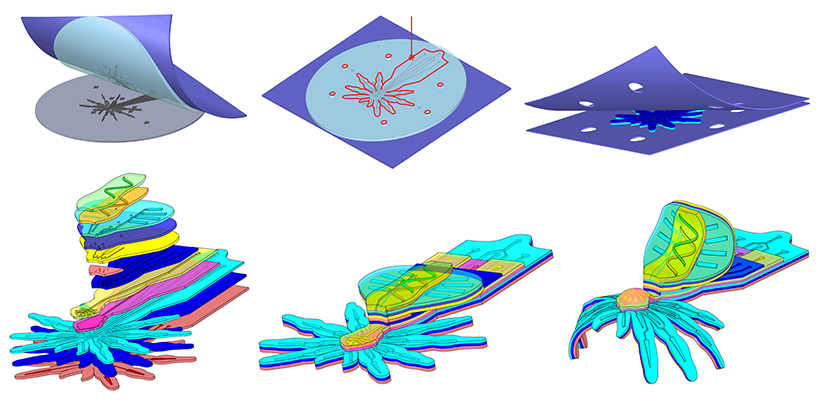
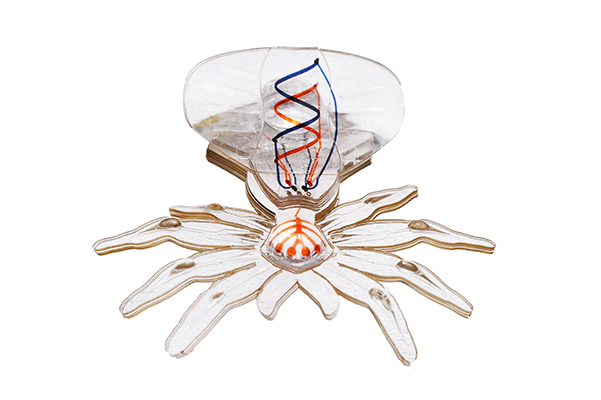
Soft Robotics
Soft Robots provide unique advantages with respect to their rigid counterparts since they are able to adapt their impedance to the surrounding environment. Such feature creates novel opportunities in the design of robotic systems able to safely operate in dynamically changing or highly unstructured environments.
We are working on strategies to design and fabricate soft robotic devices across multiple scales, from the centimeter-scale down to the micron-scale, and exploring different actuation and sensing strategies. We are also interested in strategies to tune the interaction of soft robots with the environment through variable stiffness structures embedded into the robots.
By researching materials and exploiting the capabilities of advanced manufacturing techniques, we investigate how to exploit morphological computation capabilities into our design to achieve advanced functionalities and investigate their effect on the control of the robot.
-
Soft manipulators
We are particularly interested in the potential of soft robotic technologies for designing medical tools able to safely interact and manipulate body structures.
Relevant Publications
- T. Ranzani, M. Cianchetti, G. Gerboni, I. De Falco, A. Menciassi. “A Soft Modular Manipulator for Minimally Invasive Surgery: Design and Characterization of a Single Module”, IEEE Transactions on Robotics 32(1), 2016. Video
- T. Ranzani, G. Gerboni, M. Cianchetti, A. Menciassi. “A bioinspired soft manipulator for minimally invasive surgery”, Bioinspiration & Biomimetics 10, 2015. Included in the “Highlights of 2015” collection. Video_1, Video_2
- M. Cianchetti*, T. Ranzani*, G. Gerboni, T. Nanayakkara, K. Althoefer, P. Dasgupta, A. Menciassi. “Soft robotics technologies to address shortcomings in today’s minimally invasive surgery: the STIFF-FLOP approach”, Soft Robotics. 1(2): 122-131, 2014. Featured article (*Shared first author)
- M. Li, T. Ranzani, S. Sareh, L. Seneviratne, P. Dasgupta, H. Wurdemann, K. Althoefer. “Multi-Fingered Haptic Palpation utilizing Granular Jamming Stiffness Feedback Actuators”, Smart Materials and Structures 23 095007, 2014. Included in the “Highlights of 2014” collection
- T. Ranzani, S. Russo, C. J. Walsh, R. J. Wood. “A soft suction-based end effector for endoluminal tissue manipulation”, in Proc. of 6th Hamlyn Symposium on Medical Robotics, London, UK, June 2016
-
Soft micro/meso scale robots
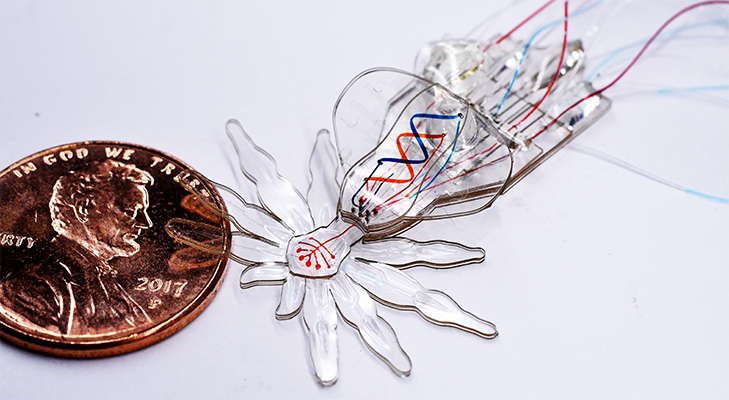
We are working on manufacturing methods to fabricate millimeter-scale soft robots to create bioinspired platforms and new soft micro robots with embedded three-dimensional microfluidic circuitry.
- T. Ranzani, S. Russo, N. Bartlett, M. Wehner, R. J. Wood. “Increasing the dimensionality of soft microstructures through injection induced self-folding“, Advanced Materials 2018, 1802739. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201802739 SI, Video
- N.R. Sinatra, T. Ranzani, V. Joost, K.K. Parker, R. J. Wood. “Nanofiber-Reinforced Soft Micro-Actuators”, Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering: Special Issue on Soft Robotics and Smart System Technologies. 28(8), 084002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6439/aab373
- S. Russo, T. Ranzani, C. J. Walsh, R. J. Wood. “An additive millimeter-scale fabrication method for soft bio-compatible actuators and sensors”, Advanced Materials Technologies. 1700135, 2017. Video_1, Video_2, Video_3
-
Soft actuators
We are looking at the design, modeling, and fabrication of soft actuators using different materials and manufacturing processes.
Relevant Publications
- T. Ranzani, M. Cianchetti, G. Gerboni, I. De Falco, A. Menciassi. “A Soft Modular Manipulator for Minimally Invasive Surgery: Design and Characterization of a Single Module”, IEEE Transactions on Robotics 32(1), 2016. Video
- Y. Elsayed, C. Lekakou, T. Ranzani, M. Cianchetti, M. Morino, A. Arezzo, A. Menciassi, T. Geng, C. Saaj. “Crimped braided sleeves for soft, actuating arm in robotic abdominal surgery”, Minimally invasive therapy & allied technologies (MITAT). 6:1-7, 2015
- Y. Elsayed, A. Vincenzi, C. Lekakou, T. Geng, C. Saaj, T. Ranzani, M. Cianchetti, A. Menciassi. “Finite element analysis (FEA) and design optimization of a pneumatically actuating silicone module for robotic surgery applications”, Soft Robotics. 1(4): 255-262, 2014. Featured article
- S. Becker, T. Ranzani, S. Russo, R. J. Wood. “Pop-Up Tissue Retraction Mechanism for Endoscopic Surgery”, The 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2017). Video.
- T. Ranzani, S. Russo, F. Schwab, C. J. Walsh, R. J. Wood. “Deployable stabilization mechanisms for endoscopic procedures”, Proceedings of Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2017 IEEE International Conference on. Video.
- S. Russo, T. Ranzani, J. Gafford, C. J. Walsh, R. J. Wood. “Soft pop-up mechanisms for micro surgical tools: design and characterization of compliant millimeter-scale articulated structures”, Proceedings of Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2016 IEEE International Conference on. 750-757, 2016. Video.
- X. Wang, T. Geng, Y. Elsayed, T. Ranzani, C. Saaj and C. Lekakou, “A new coefficient-adaptive orthonormal basis function model structure for identifying a class of pneumatic soft actuators”, 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). 530-535, 2014
-
Stiffening Mechanisms
The small Young’s modulus of soft elastomers can limit force performance for current soft robotic systems. This motivates the research into variable stiffness structures. We are interested in developing soft variable stiffness medical devices able to actively tune their compliance. By adapting their mechanical properties to the surrounding environment, they will provide safe and effective navigation inside the body, reach remote areas, and perform a surgical task.
Relevant Publications
- A. Jiang, T. Ranzani, G. Gerboni, L. Lekstutyte, K. Althoefer, P. Dasgupta, T. Nanayakkara. “Robotic Granular Jamming: Does the Membrane Matter?”, Soft Robotics. 1(3): 192-201, 2014
- T. Ranzani, M. Cianchetti, G. Gerboni, I. De Falco, A. Menciassi. “A Soft Modular Manipulator for Minimally Invasive Surgery: Design and Characterization of a Single Module”, IEEE Transactions on Robotics 32(1), 2016. Video
-
Soft Sensors
We are looking at different sensing strategies for soft robotic systems to demonstrate closed loop control of soft devices.
Relevant Publications
- S. Russo, T. Ranzani, H. Liu, N-M. Samia, K. Althoefer, A. Menciassi. “Soft and Stretchable Sensor using Biocompatible Electrodes and Liquid for Medical Applications”, Soft Robotics. 2(4): 146-154, 2015
- S. Sareh, Y. Noh, M. Li, T. Ranzani, H. Liu, K. Althoefer (2015) “Macrobend optical sensing for pose measurement in soft robot arms”, Smart Materials and Structures. 24 125024, 2015
- S. Sareh, Y. Noh, T. Ranzani, H. A. Wurdemann, H. Liu, K. Althoefer “A 7.5mm Steiner chain fiber-optic system for multi-segment flex sensing”, 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). 2336-2341, 2015
- S. Sareh, Y. Noh, T. Ranzani, H. Wurdemann, H. Liu, K. Althoefer “Modular fiber-optic shape sensor for articulated surgical instruments”, in Proc. of 5th Hamlyn Symposium on Medical Robotics, London, UK, June 2015
- B. Quinlivan, A. T. Asbeck, D. Wagner, T. Ranzani, S. Russo, C. J. Walsh. “Force Transfer Characterization of a Soft Exosuit for Gait Assistance”, in Proceedings of the ASME 2015 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference (IDETC/CIE 2015). Boston, USA, 2015
- L. Ricotti, T. Ranzani, V. Calarota, A. Menciassi. “Thin and Flexible Contact/Deformation Sensors Based on Piezoelectric Nanocomposites”, SENSORS, 2014 IEEE . 2070-2073, 2014
- Y. Noh, S. Sareh, J. Back, H.A. Wurdemann, Ranzani T, E.L. Secco, A. Faragasso, H. Liu, K. Althoefer. “A Three Axial Body Force Sensor for Flexible Manipulator”, Proceedings of Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2014 IEEE International Conference on. 6388-6393, 2014