What We Think We See – Why the Real World is Confusing
Most of us rely on our eyes in order to help us interact with the world on a daily basis. Yet the visual system often distorts what we see, so what we think we see is actually an altered reality. According to Dr. Mareschal, as quoted in an article published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, “[i]n fact a lot of it is distortion, and it is occurring in the early processing of the brain, before consciousness takes over. Our [researchers from the University of Sydney’s School of Psychology and The Vision Centre] work shows that the cells of the primary visual cortex create small distortions, which then pass on to the higher level of the brain, to interpret as best it can…And we found that even the higher brain cannot always correct for them, as it doesn’t in fact know they are illusions.”
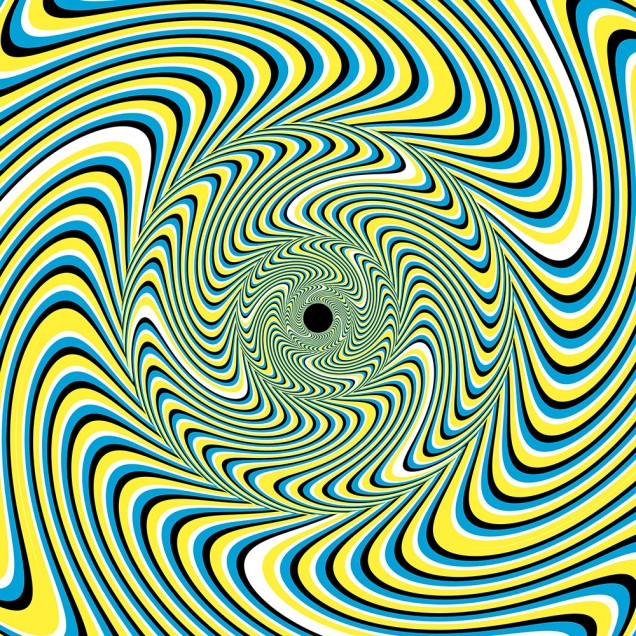
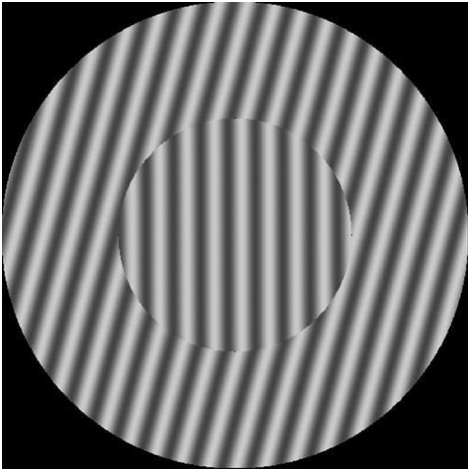
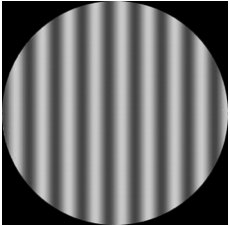
In agreement with previously discovered results, Dr. Mareschal and her colleague Professor Clifford found that these illusions were occurring during early processing in the brain, prior to consciousness. They then went on to be the first labs to report being able to connect the origin of the tilt illusion to the cells of the primary visual cortex, a highly specialized region in the occipital lobe of the brain. Let me take this chance to explain what the tilt illusion is. Take a look at this image before reading on:
What direction do the lines of the inner circle appear to be rotated in: clockwise, counterclockwise, or not at all? Notice how the lines in the inner circle appear to be tilted counterclockwise. Here’s the catch though: they’re actually vertical.
Why is this? According to Mareschal and Clifford, the brain looks to the surroundings for contextual information in order to determine the pattern and alignment of an image. Therefore, because the lines in the outer circle are tilted clockwise and because the lines in the inner circle are tilted away from those of the outer circle, the brain concludes that they must be sloped counterclockwise, while the truth is they are simply vertical.
Here is an example of how our brain utilizes context clues to help us form images in our brain: What are these broken pieces a part of?
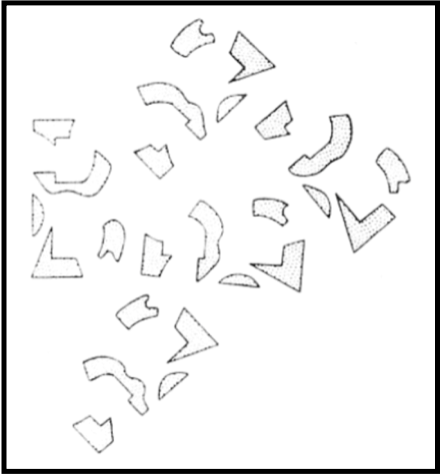 Via Ink Covered Optical Illusions
Via Ink Covered Optical Illusions
Can you see it now?
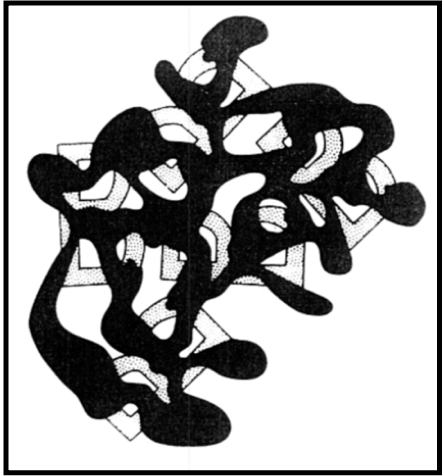 Via Ink Covered Optical Illusions
Via Ink Covered Optical Illusions
The only thing that changed between the first picture and the second picture is the presence of the spilled ink. In the first image, there is too much empty space for the brain to piece together the image because the missing pieces of the image and the background are both white. However, in the second image, the black ink connects the pieces of the image, allowing our brain to put them together into a familiar object – the letter B. Here, we use the presence of contextual clues to trick our brains into recognizing the image.
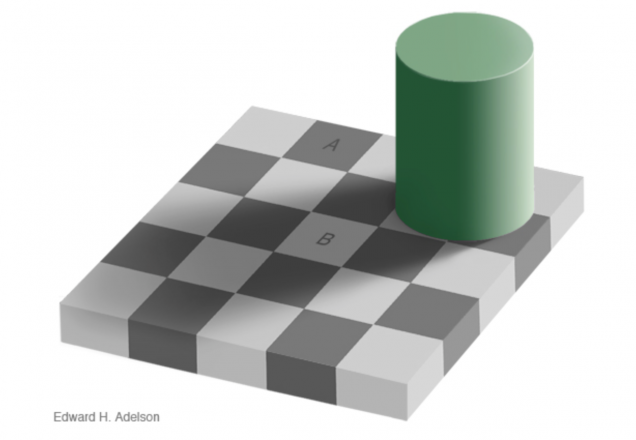
Here is a final example of how our brain can be tricked by contextual information: Is square A or square B darker?
 Via mit.edu
Via mit.edu
Trick question! The two squares are actually the same shade of grey, despite the fact that they appear different. We are able to see this by connecting the two squares with grey strips of the same shade throughout.
 Via mit.edu
Via mit.edu
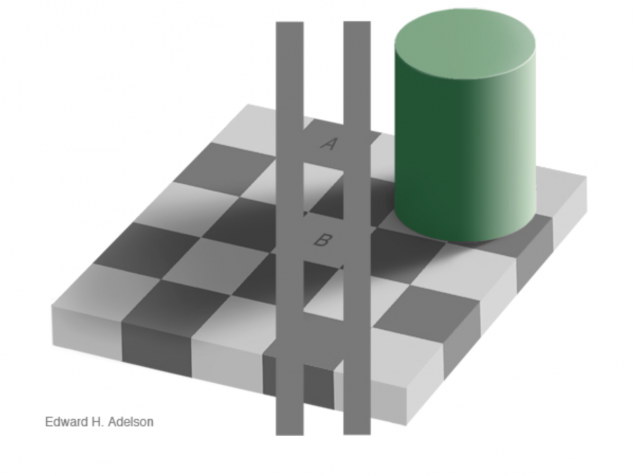
In order to explain this, we need to discuss the successes demonstrated by our visual system as well as the failures while interpreting this image. Notice that square A is supposedly a dark checker and square B is a light one. Due to the arrangement of squares on a checkerboard, lighter checkers will be surrounded by darker checkers and, likewise, darker checkers will be surrounded by lighter ones. Despite the presence of the shadow, ultimately making all of the checkers within the shadow a “darker shade of paint,” square B is still surrounded by darker tiles. This contextual information cues our brain to recognizes B as a light checker and A as a dark one, although we have now proven that they are actually the same shade of grey.
So to summarize: “All I know is that I know nothing” ~ Socrates
~Alexa Aaronson
Sources:
Professor Gavornik’s Principles of Neuroscience Lectures – Thanks!
Image Source:
Sonic Hedgehog and Astrocytes
During our introductory neuroscience courses, we’re taught that the brain has very poor healing capabilities following an injury. This has always stuck with me because of how terrifying it sounds—if something happens to your brain, it’s pretty much goodbye to that part of the brain. Putting this harrowing thought aside, new research has shown that astrocytes, star-shaped neurons, are of a greater adaptability and plasticity than what was originally believed, playing an important role in healing the brain following an injury.
A study performed at McGill University revealed that following an injury, surrounding neurons can adjust astrocytes in a way similar to the turning of a dial, changing the function and capabilities of the astrocyte. The Researchers used Bergmann glia, a type of astrocyte, and Purkinje cells, a neuron that secretes a protein referred to as Sonic Hedgehog, to study these effects. They found that the release of this specially named protein induces significant changes in astrocytes that promote healing.
This discovery is significant for two reasons: firstly, we believed the brain to have very poor recovery capabilities and secondly, we formerly believed that neuronal cells were hardwired during development to perform a single, specific function. Both of these are wrong. Not only does this study show that astrocytes are quite active in neural healing, but it also shows that they are not limited to one specific function, and can adapt to whatever the environment demands based on the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway.
On a personal level these findings are exciting because maybe it means I don’t need to be as paranoid about getting a head injury. Sonic the Hedgehog is on my side if anything bad goes wrong up there.
~Jackie Rocheleau
Sources:
A Key Mechanism that Could Improve Brain Function
Neurons Diversify Astrocytes in the Adult Brain Through Sonic Hedgehog Signaling
Image Source:
The Effects of Caffeine on the Mind
Coffee. Tea. Energy drinks. Almost everyone drinks at least one to get an energy boost; we have caffeine, the active ingredient in such beverages to thank for that boost. But how exactly does caffeine work – how does it affect the brain and its functions?
Caffeine is considered a stimulant; the drug temporarily improves either mental functions, physical functions, or both. Studies performed by the European Food Safety Authority show that there is a cause and effect relation between improved alertness, attention, and concentration, and 75mg of caffeine (the amount in a regular cup of coffee). The energy boost obtained from caffeine comes from a multitude of neural circuits becoming activated, resulting in the release of adrenaline - the “fight or flight” hormone - from the adrenal gland. Some studies also show that caffeine improves memory based performance, although excessive intake may actually decrease performance, possibly due to overstimulation.
Despite improving mental performance, caffeine has been shown to negatively affect sleep patterns, because the drug reduces the activity of the neuromodulator adenosine, which is responsible for facilitating sleep and slowing down neural activity. Research suggests that if one’s sleep quality declines as a result of high caffeine intake, one can regain sleep quality by abstaining from caffeinated beverages for a whole day.
According to the World Health Organization and several studies, caffeine does not induce dependence. In fact, brain mapping technology shows that caffeine is not linked to the brain's circuit of dependence. However, caffeine increases the production of dopamine in the brain’s pleasure circuits so that abrupt cessation of caffeine consumption may lead to withdrawal symptoms in some regular caffeine consumers, resulting in headaches, reduced awareness, and drowsiness. These symptoms are generally not severe though, and are transient. If caffeine intake is decreased progressively instead of abruptly, these symptoms can be avoided altogether.
~Nathaniel Meshberg
Sources:
How Drugs Affect Neurotransmitters
Image Source:
Toxicity of Amyloid Bundles and Why Size Matters
Amyloid Beta Plaques are bundles of protein that accumulate at certain locations within the body, commonly leading to Alzheimer’s Disease, and sometimes other diseases. As a result, scientists are trying to study Amyloid Beta proteins to understand the disease, and any other neurodegenerative diseases related to Alzheimer’s Disease. As for whether the protein itself is toxic or not, that depends on the shape of the Amyloid beta. Amyloid beta (ABeta) only becomes toxic when it forms small bundles, and it become less toxic as they form larger fibrillar structures. The effects of shape on toxicity were discovered by the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research in India, where scientists used nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and froze the samples of ABeta to determine the structure during the different times of evolution. They also found that the toxicity begins to occur due to a transition from intramolecular to intermolecular beta sheets, which makes them less toxic. Discovering how to manipulate the toxic form may ultimately lead to the reduction in the toxicity of certain drugs and also a greater understanding of the molecular basis of man diseases.
Another way to reduce plaque formation is with a new candidate for a drug - a molecule in snake venom that is able to activate the enzymes that break down the plaques in the brain. It was recently discovered by Dr. Sanjaya Kuruppu and Professor Ian Smith from Monash University’s Biomedicine Discovery Institute that this one molecule was able to enhance the enzymes' ability to break down plaque in the venom of a pit viper from South America. As more discoveries are being made about amyloid beta plaques, we get closer to unraveling its molecular mystery, and hopefully soon we will be able to reduce the harmful side effects of certain drugs or even prevent neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s from occurring at all.
~Albert Wang
Sources:
The Evolution of Amyloid Toxicity in Alzheimer’s
Snake Venom May Hold Key to Breaking Down Alzheimer’s Plaques
Platform: Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDP) and Aggregates II
Image Source:
A Big Future for Mini-Brains
Recently, a team of researchers from Johns Hopkins University developed “mini-brains” from human skin cells that could replace animal models in drug research. The lead researcher, Thomas Hartung, asserts that “the future of brain research will include less reliance on animals, more reliance on human, cell-based models” such as this new method. Miniature brains produce electrical activity similar to real brains. These small bundles of cells “[represent] more or less a two-month-old brain.” Researchers have standardized the mini-brains and can cultivate one hundred identical brain cultures in one petri dish.
The mini-brains were developed from five donors’ skin cells, genetically programmed to produce induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which are adult cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to “blank slate” cells and then stimulated to develop into brain cells. Since mini-brains are cultivated in dense clusters, they electrically stimulate one another. The mini-brains develop over the course of eight weeks and grow to about 350 micrometers in diameter. They consist of four different types of neurons found in the human brain. They also contain two types of support cells: astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Astrocytes support neurons, and oligodendrocytes create myelin, which insulates axons and facilitates neural communication. Researchers can observe myelin development as it starts to sheath the axons. The spontaneous electrophysiological activity of these structures can be measured using a device similar to the EEG, an electrode array, which allows researchers to study the electrical activity of the mini-brains when they are exposed to various drugs. Hartung suggested that specific mini-brains could be developed using the cells of people with conditions caused by both genetic and environmental factors, such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and autism, to study the effect of drugs on these traits.
Mini-brains have the potential to revolutionize how drugs are studied. Using animal models in studying the effects of drugs has always been controversial. There are various ethical reasons to consider when using animals. In addition, since human brains are different from the brains of other species in various ways, the results of animal models often do not apply to humans. Since the mini-brains develop from human cells, the results obtained from these new studies may be more reliable than current animal models.
~Sophia Hon
Sources:
Researchers Create ‘Mini-Brains’ in Lab to Study Neurological Diseases
‘Mini-Brains’ Could Revolutionise Drug Research and Reduce Animal Use
Lab-Grown “Mini-Brains” Could Aid Drug Research
Image Source:
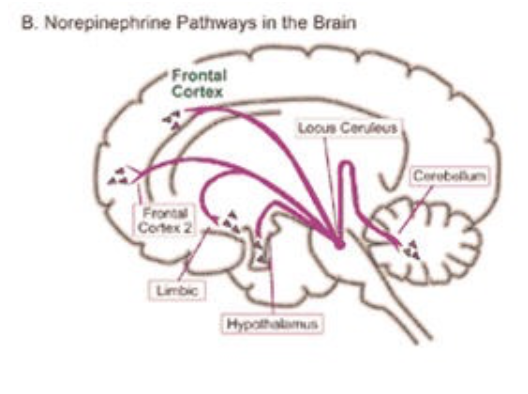
Ground Zero in Alzheimer’s Disease
Research in Alzheimer’s disease has been prevalent in recent years and still has been flourishing until now. Recently, a new breakthrough has been discovered in the research of Alzheimer’s: the ground zero has been discovered. This ground zero is where the origin of Alzheimer’s starts and where it begins its development, in a region called the locus coerleus. The locus coerleus has its role in many of the body’s systems, such as that regarding attention, memory, and cognition function. Its main role is to produce norepinephrine, which is the neurotransmitter responsible for the fight or flight response. This locus coerleus has shown tau protein build up in its beginning stages, appearing as early as adolescence, signaling the first symptoms of Alzheimer’s. Although it was already known that the locus coerleus was involved in the disease, it was only recently discovered that this was the starting point of Alzheimer’s.
This new breakthrough has many implications in how we can treat Alzheimer’s and it further supports previous studies. The Nun Study, a longitudinal study that followed 678 Catholic sisters and studied whether they showed signs of Alzheimer’s disease, is an example of a preceding study that supported cognitive reserve theory. Because, as discussed before, the starting point for this disease is the locus coerleus and the main neurotransmitter released from here is norepinephrine, training the cognitive reserve by reading books and keeping the memory system working will ultimately decrease the chances of getting Alzheimer’s. Hopefully this breakthrough will result in further advances in the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease and maybe, one day, we will find a cure.
~Albert Wang
Sources:
Healthy Aging and Dementia: Findings from the Nun Study
Researchers Highlight Brain Region as ‘Ground Zero’ of Alzheimer’s Disease
‘Ground Zero’ of Alzheimer’s: Locus Coeruleus Identified as Critical Starting Point of Disease
Image Source:
Weeding Out the Problem
Sometimes harmful drugs can lead to fruitful discoveries. At the University of Texas, neuroscientists have found that marijuana impinges upon the development of higher order cognitive structures depending on the age at which the user began using marijuana regularly. This study gives us important insight on not only the effect of hallucinogens, but more importantly about the development of the adolescent brain, a staggering mystery even to adolescents.
Most judgment and complex thinking occurs in the prefrontal cortex, the area right behind your forehead. From the study, it was found that those who started using marijuana at 16 years old or younger had much slower development in the prefrontal cortex. But, for those who started using after the age of 16, the brain actually aged faster. The age at which you start using marijuana affects the type of deficiencies the drug causes.
By examining MRI images of subjects’ brains, the research team made several interesting discoveries. It is known that during the teenage years, the brain goes through a lot of changes, including pruning neuronal connections, thinning of the cortex, and creating more folds that give that nice, wrinkled look you want. This phenomenon, knows as gyrification, wasn’t seen in those who used marijuana before the age of 16 to the same extent as those who used after that age. Those who started using after 16 had issues later in life and actually had the opposite problem—too little cortical thickness and too much gray-white matter contrast.
Interestingly, this study shoes that marijuana affects the brain during adolescent development far more than alcohol does. The active ingredient in marijuana, THC, binds to receptors that normally accept a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, anandamide. The higher than usual amount of activity at these receptors then eventually results in depletion of the receptors, leading to the cognitive deficits often seen in users. Alcohol is quite different, bonding to many different receptors and causing certain receptors to become hyper-sensitized or desensitized. The differences in the way these two drugs act accounts for their different affects on the brain, and possibly the difference in the severity of their affects.
~ Jackie Rocheleau
Sources:
How Drugs Affect Neurotransmitters
Starting Age of Marijuana Use May Have Long-Term Effects on Brain Development
Image Source:
The Reflex to Catch Arrows: Real or Impossible?
The award-winning “Kung-Fu Panda” franchise is one of my all-time favorite movies. One of the most intriguing moments in the second film is the scene in which Mistress Tigress, the main protagonist’s assistant, catches a soaring arrow with her bare hands. This incredible act in the movie prompted me to explore the question of whether this would be possible in real life and the brain mechanisms that would be involved.
Catching an arrow with her bare hands may initially be a voluntary act, but through repeated association of the stimulus with a desired outcome and lots of practice, Mistress Tigress has trained this voluntary act to become an involuntary reflex. Involuntary movements are automatic muscle responses to stimuli. The brain controls the activity of motor neurons and muscles in order to create immediate responses. Most involuntary responses are processed in the spine. The spinal nerve consists of two main roots: the ventral and dorsal roots. The ventral roots control the movement of the body’s muscles as the signs are sent by the brain’s primary motor cortex. The dorsal roots do the opposite: they create signals to the ventral roots via analysis of the body senses. This exchange of corporeal information is reflex.
In addition to the ability to control movement and reflexes, the brain also has amazing neuroplasticity, which allows it to adapt and acquire strengths in certain regions of the brain. Due to consistent training and practice, Mistress Tigress’s brain is likely to have more neural pathways in specific brain regions responsible for her Kung Fu skills, such as the motor cortex.
While it is certainly a difficult act, catching an arrow with your bare hands may be possible with years of training and strong mental focus because of the brain’s neuroplasticity and the spinal nerve’s amazing ability to process the mechanisms behind reflexes.
~ Dongjun Yoo
Sources:
Testing and Comparing Bows by Measuring Arrow Speeds in Feet per Second
Introduction to the Nervous System; Peripheral Nervous System
Image Source:
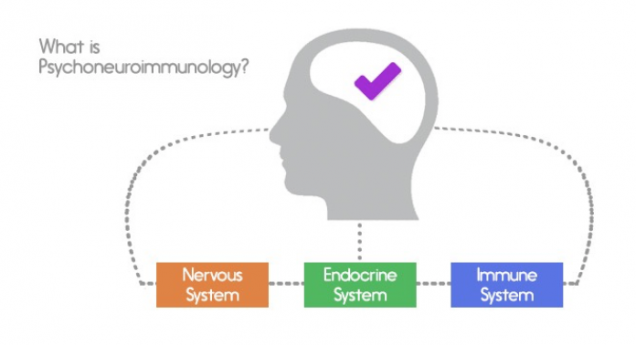
Psychoneuroimmunology: A New Approach to Curing Diseases
When one thinks of disease and cures for it, people typically think medicine or other pharmacological interventions to prevent the disease from spreading or killing it entirely. People also tend to associate physical symptoms as being mainly in part due to the immune system and have little regard toward the neurological approaches to the disease. Now over the past decade, a new approach to diseases is surfacing and gaining more evidence as time goes on: psychoneuroimmunology. Psychoneuroimmunology is a new approach to diseases which involves taking control of the disease by controlling stress and lessening it. Diseases and illnesses untreatable by drugs or medicine could be treated by just understanding and influencing the psychology of the given individual. Psychology has an impact in grieving, cancer, HIV, and wound healings, making it possible for the patient to not suffer in pain but gradually heal over time or increase their outlook on life.
Robert Adler, father of psychoneuroimmunology, first discovered this when he was working on different experiments using Pavlonian conditioning where he involved rats. He found out the conditioning had both a psychological effect via avoidance as well as a neurological and biological effect, as the effects of the drug were shown through both the injected and non-injected rats. From this psychoneuroimmunology was born. As research progressed, more evidence was found, such as in 1981 in David Felten’s lab where he found a relationship between nerves and the cells of the immune system, showing that they actually contact each other directly, through the HPA Axis, which are the glands that secrete hormones in your blood. Ultimately, they are all determined by one’s stress levels.
There have been more studies proving psychoneuroimmunology’s effects on the conditions and immune system of the body. On August 2012, it was reported that Steve Cole, member of the Cousins Center for Psychoneuroimmunology, conducted a study where they ran a mindfulness-based stress reduction study, where patients were told to focus on now and not about the future or the past. This not only reduced lonely feelings, but also altered gene and protein markers of inflammation, which, if accumulated, could lead to the risk of heart disease, showing its overall effect on the immune system. Another study by the same group was also conducted which found that those with a meaningful or purposeful outlook on life had a better gene expression than those who were materialistically happy or those who were facing problems. While this is a study of much needed research, many advances are being made in this new and exciting field.
~ Albert Wang
Sources:
Psychoneuroimmunology: Laugh and Be Well
Meditation Reduces Loneliness and Expression of Inflammatory Genes
Immunology: The Pursuit of Happiness
Photo Source:
The Science Behind Senioritis
We’ve all heard of Senioritis - “a general apathy towards school work that is developed after years of schooling at an institution” (McMullen). However, is this an actual biological phenomenon? Or is it simply an excuse for lazy students to not work hard anymore? The answer may be a bit of both. Although there are ways to overcome Senioritis, research suggests that levels of dopamine in the brain can be linked to whether a person is a slacker or a go-getter.
According to a study put forth by Vanderbilt University, high levels of dopamine in many regions of the brain are associated with a high work ethic. However, there is a strong negative correlation between dopamine levels and work ethic in the anterior insula. The results of this study showed that hardworking people have high levels of dopamine in the two parts of the brain most known for their role in reward and motivation, and low dopamine levels in the anterior insula, which is linked to motivation and risk perception. Therefore, these results may mean that the choice between being a slacker or a go-getter is actually dependent on how the brain weighs risks and rewards. Perhaps then Senioritis could actually be explained by a change in dopamine levels in the three noted regions of the brain. Unfortunately, more research would be needed in order to support this conclusion.
Meanwhile, how do we, exhausted seniors who are ready to move on with our lives, push past Senioritis in order to perform to the best of our ability and enjoy what’s left of this last semester of our college careers? Here are 5 ideas that you may find helpful:
1) Challenge yourself to try something new every week. Whether they be on campus or in the community, chances are there are many events going on every week that you don’t even know about. Take the time to search for something new to do, and then challenge yourself to go with an open mind. Not only would that push you out of your comfort zone and possibly even get you out of your funk, but you could also discover a new passion or hobby.
2) Do something physical. Often times, feeling apathetic can make us feel physically tired. Not only will exercising improve your health, but it can also help you de-stress and increase your energy.
3) Mentor an underclassman. By the time you are a senior, you (hopefully) have quite a bit of it all figured out. You’ve learned what it takes to succeed and what to strive towards. Share this knowledge with others who may be struggling to figure it out on their own. Not only will this help them, but it will also help you reflect on how far you’ve come and, hopefully, will allow you to regain some perspective.
4) Start early. I know - procrastination and senior year seem to go together like a lock and a key. However, procrastination can be the difference between graduating and spending an extra semester in college because you failed a class. It’s not worth it! Plus - and I know I’m about to sound like your mother here - the sooner you finish your work, the sooner you can go out with friends and enjoy the rest of your college time together.
5) Stay organized. Know your goals and create a strategy to achieve them. Create a calendar with all of your classes, volunteering, work, office hours, exams, and homework due dates, along with anything else you need to remember. Set reminders on your phone or write yourself notes and tape them all over your room (Yes Mom, I did learn eventually) - whatever works for you. Make sure to check your schedule for the next day the night before to make sure you aren’t forgetting anything.
Most importantly though, enjoy your senior year! We are about to undergo a major life change that not everybody has the privilege of having. Try to appreciate what you have and take advantage of every opportunity you can. Work hard, make memories, and follow this link for a countdown to BU’s commencement ceremony!
Good luck Seniors! We’re almost there!
~ Alexa Aaronson
Sources:
5 Tips to Battle College Senioritis
Slacker or Go-Getter? Brain Chemical May Tell