Where We Are
Africare and MAHMAZ are each implementing the Core Mothers’ Shelter Intervention Model in Southern, Eastern and Luapula Provinces at a total of 20 primary health facilities, through their respective projects: Africare’s Zambia Mothers’ Shelters (ZaMS) and BU’s Maternity Home Access in Zambia (MAHMAZ). The intervention targets all pregnant women within 1-2 weeks of estimated delivery date (EDD) resident within the facility catchment areas, particularly those living furthest from care (i.e. > 9.5 km from the health facility).
All study sites have a minimum standard of available care, defined as either A or B, below:
Criteria for A:
- Able to provide at least 5 of 7 basic emergency obstetric and newborn care (BEmONC) signal functions
- <2 hours travel time to a comprehensive emergency obstetric and newborn care (CEmONC) referral facility, and
- Have a minimum of 150 deliveries per year
Criteria for B:
- At least one skilled birth attendant (SBA) on staff
- Routinely provide active management of third stage of labor (AMTSL)
- No stock outs of oxytocin in the last 12 months
- No stock outs of magnesium sulfate in the last 12 months, and
- <2 hours travel time to a CEmONC referral facility
| Figure 1. Map of Intervention and Comparison Sites Across MSA |
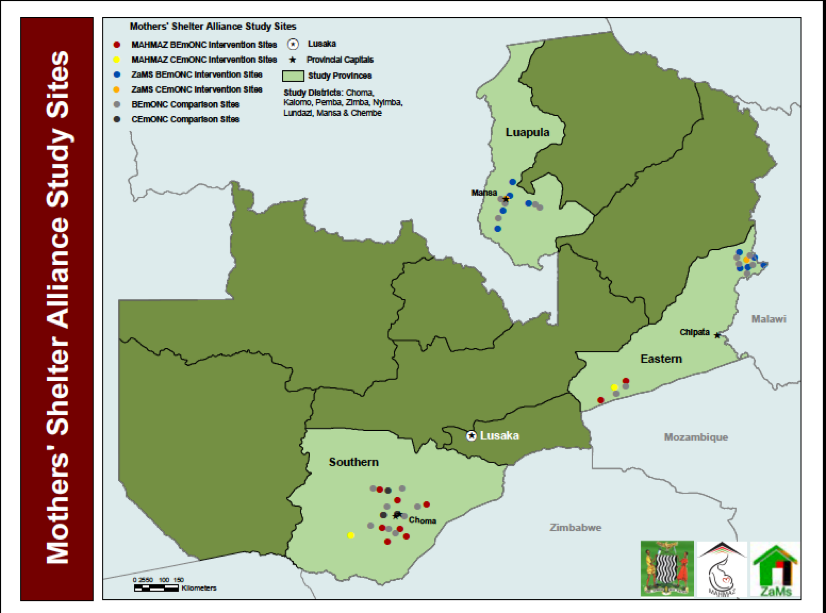
To select study sites, both implementing partners developed a list of sites that met either Criteria A or B above. MAHMAZ then selected the 20 sites farthest from CEmONC. These were then divided into 10 pairs matched on transfer time to CEmONC and clinic delivery volume. Pairs were then randomized into the intervention or control group, yielding 10 intervention and 10 control sites.
ZAMS purposively selected 10 intervention sites and identified 10 comparison sites, matched on transfer time to CEmONC and clinic volume. This totals 20 intervention and 20 comparison sites across the MSA as seen in Figure 1 (see full list of sites and maps, Annex 2). All study sites were selected in Districts that are supported by the SMGL program. In interventions sites, MSs were constructed/renovated based on community standards as outlined in Figure 2. Comparison sites received standard of care, with or without an existing MS.