Field Sites
Harvard Forest (2007)
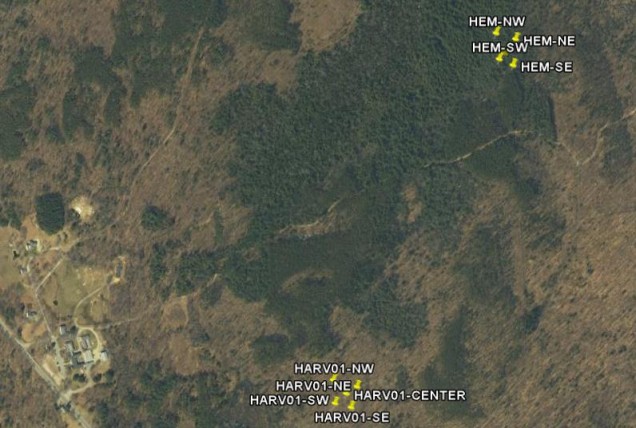
Harvard Forest is located in the central Massachusetts town of Petersham with 1200 ha area, the Forest’s varied habitats are typical of those found throughout New England . Since 1907 research and education has been the mission of the Harvard Forest , one of the oldest and most intensively studied forests in North America .
There are four main tracts in Harvard Forest : Prospect Hill tract, Tom Swamp tract, Slab City tract and Simes tract. Our research locates in Prospect Hill tract, which is in northeast of Harvard Forest . Two sites are chosen as the Echidna scanning area. One is Deciduous stand and the other is Hemlock stand. The dominant species include red oak (Quercus rubra), red maple (Acer rubrum), black birch (Betula lenta), white pine (Pinus strobus), and hemlock (Tsuga canadensis).
Howland Forest (2007)
The Howland Forest research site is located in central Maine and about 35 miles north of Bangor at 45° 12′ N, 68° 44′ W at an elevation of 60 m, west of the town of Howland. Red spruce.
Originally established by the University of Maine within International Paper’s Northern Experimental Forest, Howland forest site covers about 7000 hectares, including several intensive experimental sites, has a well-instrumented 25 meter flux tower, and has been made part of the Ameriflux network of flux measurement sites. This site has been chosen by NASA’s Forest Ecosystem Dynamics (FED) project, NOAA’s Atmospheric Turbulence and Diffusion Division, and the Wood’s Hole Research Center for research site in that it is representative of boreal transitional forest. The natural stands in this boreal-northern hardwood transitional forest consist of hemlock-spruce-fir, and hemlock-hardwood mixtures. The region has relatively little topographic relief, but soil drainage classes vary greatly over short distances.
Bartlett Forest (2007)
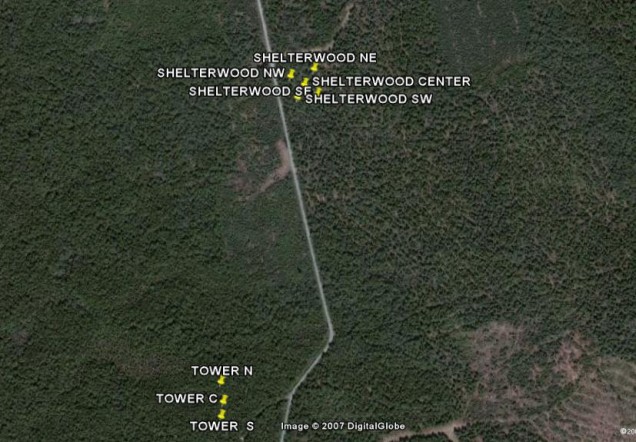
As the field laboratory for research on the ecology and management of northern hardwoods and associated ecosystems, Bartlett Experimental Forest (BEF) is located within the Saco Ranger District of the White Mountain National Forest in New Hampshire. There are areas of old-growth northern hardwoods with beech, yellow birch, sugar maple, and eastern hemlock being the dominant species. Even-aged stands of red maple, paper birch, and aspen occupy sites that were once cleared. Red spruce stands cover the highest slopes. Eastern white pine is confined to the lowest elevations. There are also oak types which are fairly common nearby on southerly and westerly slopes. All of species above have composed the major plant communities in BEF.
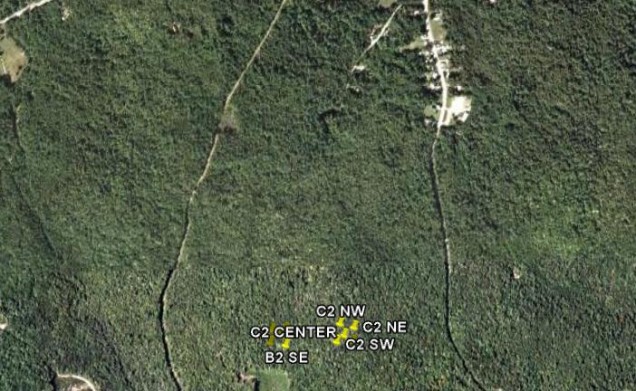
This particular site was chosen because it represented the tree species composition typical of many forested areas throughout New England and northern New York. In addition, the TRAC measurements and LAI2000 measurements from North America Carbon Program on this site can also provide us a good data comparison. We had basically chosen 2 sub sites here, with one of them (Site B2) quite close to the tower of BEF and the other one (Site C2) which is about 220 meters east. The main tree species in Site B2 are red maple, with some white pine, beech and birch trees. For Site C2, the beech trees are the major species mixed with eastern hemlock, red maple and white pine. The topography in both sub sites are not too steep, expect that there is a small hillock near the center of the Site C2 with trees growing on it. Site B2 has comparatively more under story canopies than Site C2.
Sierras Forest (2008)
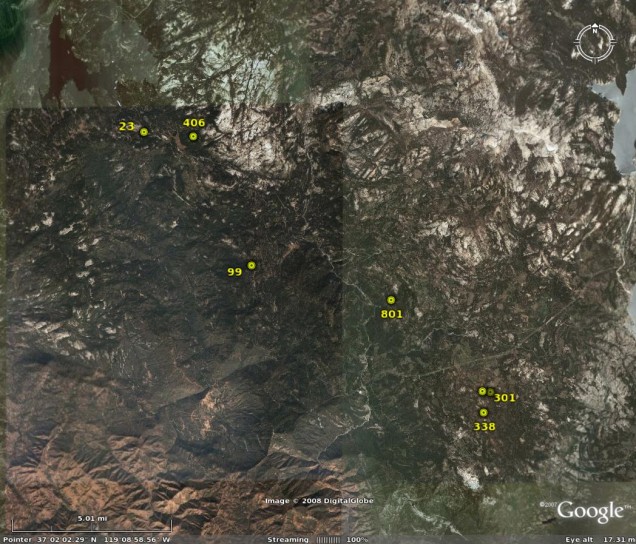 The Sierra National Forest, located on the western slope of the central Sierra Nevada, encompasses more than 1.3 million acres (5,300 km2), between 900 and 13,986 feet (300 to 4,300 m) in elevation. The terrain includes rolling, oak-covered foothills, heavily forested middle elevation slopes and the starkly beautiful alpine landscape of the High Sierra. The Sierra National Forest is best known for the giant sequoias (redwood trees) of the Nelder and McKinley groves and the High Sierra, Minarets, and John Muir wilderness areas.
The Sierra National Forest, located on the western slope of the central Sierra Nevada, encompasses more than 1.3 million acres (5,300 km2), between 900 and 13,986 feet (300 to 4,300 m) in elevation. The terrain includes rolling, oak-covered foothills, heavily forested middle elevation slopes and the starkly beautiful alpine landscape of the High Sierra. The Sierra National Forest is best known for the giant sequoias (redwood trees) of the Nelder and McKinley groves and the High Sierra, Minarets, and John Muir wilderness areas.
Laser Vegetation Imaging Sensor (LVIS) has flown over Sierra National Forest (CA, USA) in 1999 and 2003. Field data for this study were collected in the summer of 2008 in the Sierra National Forest as part of one on-going research studies conducted by Boston University, CSIRO Australia,University of Maryland, Hunter College of CUNY and Beijing Normal University.