Research
The Problem
Photovoltaic (PV) plants and Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) installations suffer losses in output power due to the natural deposition of dust on the solar collectors’ surface, a phenomenon termed as “soiling”. Soiling losses can amount to 5 to 70% loss of the annual power output unless the modules are cleaned frequently. Fresh water needed for cleaning solar collectors of utility-scale solar plants can cause a major negative impact in many areas of the world suffering from water scarcity. If solar power is to grow to the terra-watt level capacity as predicted, there is not enough fresh water available in semi-arid and desert areas of the world to clean the solar collectors.
The EDS
The Electrodynamic Screen (EDS) film consists of interdigitated, parallel electrodes in a 3-phase design that when activated by pulsed voltages generates a traveling electric field, which charges and sweeps the dust particles from the module surface, with no moving parts or water requirement.
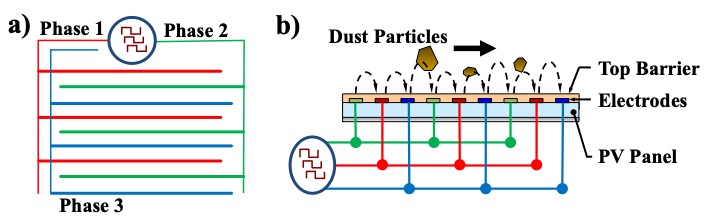
When activated for under two minutes, the EDS film can restore the output power of a PV panel to over 95% of its original power output.
- EDS films can be integrated directly onto the front optical surface of a PV module or retrofitted in a solar field.
- Energy requirement for cleaning is small, less than 0.02 W/m2/cleaning cycle.
- EDS film prototypes are screen printed in the lab and/or produced using flexographic printing at Eastman Kodak Company using their existing roll-to-roll manufacturing plant.
- The EDS films’ electrodes are protected by a transparent dielectric film that acts as the top surface.
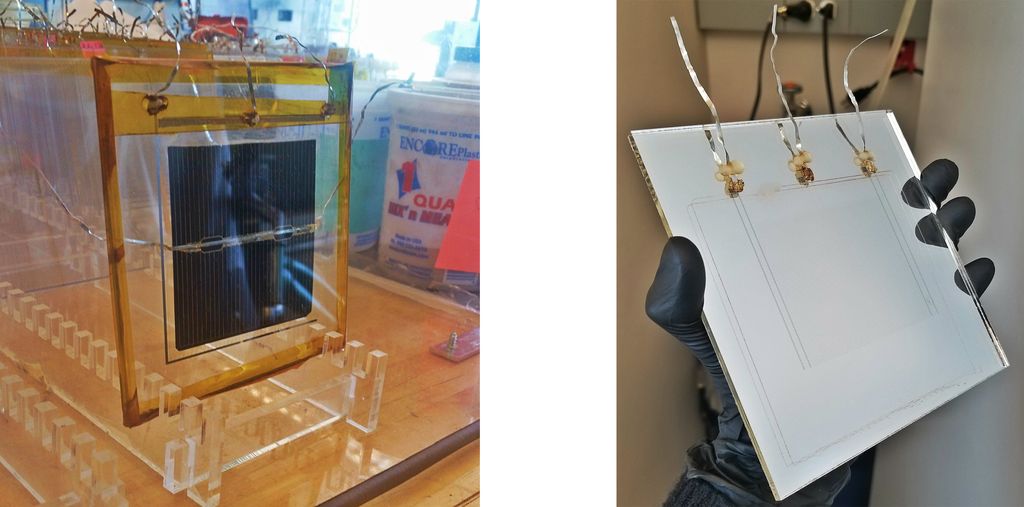
Integration with PV
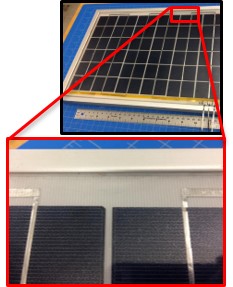
The EDS film can be integrated as a component of a PV module during initial fabrication. The mechanical flexibility of the EDS film also enables after-market retrofitting. Integration of the EDS has multiple benefits.
- Increase the power output by allowing frequent, on demand cleanings.
- Reduce the O&M cost of operating a solar plant by mitigating soiling losses
- Minimize consumption of water