Ground Zero in Alzheimer’s Disease
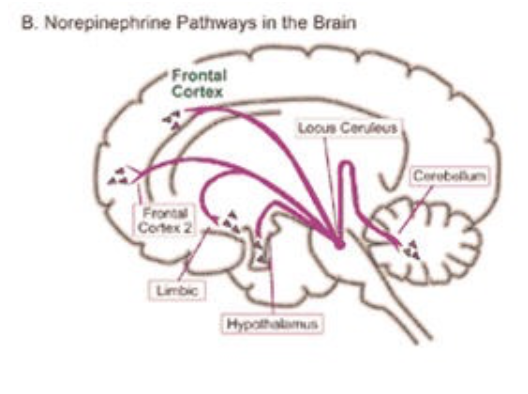
Research in Alzheimer’s disease has been prevalent in recent years and still has been flourishing until now. Recently, a new breakthrough has been discovered in the research of Alzheimer’s: the ground zero has been discovered. This ground zero is where the origin of Alzheimer’s starts and where it begins its development, in a region called the locus coerleus. The locus coerleus has its role in many of the body’s systems, such as that regarding attention, memory, and cognition function. Its main role is to produce norepinephrine, which is the neurotransmitter responsible for the fight or flight response. This locus coerleus has shown tau protein build up in its beginning stages, appearing as early as adolescence, signaling the first symptoms of Alzheimer’s. Although it was already known that the locus coerleus was involved in the disease, it was only recently discovered that this was the starting point of Alzheimer’s.
This new breakthrough has many implications in how we can treat Alzheimer’s and it further supports previous studies. The Nun Study, a longitudinal study that followed 678 Catholic sisters and studied whether they showed signs of Alzheimer’s disease, is an example of a preceding study that supported cognitive reserve theory. Because, as discussed before, the starting point for this disease is the locus coerleus and the main neurotransmitter released from here is norepinephrine, training the cognitive reserve by reading books and keeping the memory system working will ultimately decrease the chances of getting Alzheimer’s. Hopefully this breakthrough will result in further advances in the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease and maybe, one day, we will find a cure.
~Albert Wang
Sources:
Healthy Aging and Dementia: Findings from the Nun Study
Researchers Highlight Brain Region as ‘Ground Zero’ of Alzheimer’s Disease
‘Ground Zero’ of Alzheimer’s: Locus Coeruleus Identified as Critical Starting Point of Disease
Image Source: