Research and Publications
1. Study the cascade of intracellular events that leads to the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling
Since the Wnt pathway was first identified, a number of studies in many animal models and in vitro have delineated an intracellular pathway made of core components including receptors, positive regulators like Dvl, negative regulators Axin and Apc, and co-transcriptional activators β-catenin and TCF/LEF. In addition, a number of other components that modify the activity, stability or localization of these core components have been identified. Despite these advances, our understanding of the molecular mechanism of Wnt/β-catenin signaling is not complete, and a number of steps have not been fully characterized, including the mechanism of β-catenin and Dvl activation.
We have shown that CK2 is essential for Wnt/β-catenin signaling in Xenopus laevis embryos and cell lines. Biochemical experiments indicate that CK2 acts through phosphorylation of the core Wnt/β-catenin components β-catenin and Dvl. Therefore, we are characterizing the molecular mechanism leading to activation of Dvl and β-catenin, the key intracellular Wnt/β-catenin signaling component that is upregulated in many human tumors. As we acquire a better understanding of the molecular events leading to Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation, we will be able to develop novel and specific inhibitors for the treatment of cancers with upregulated nuclear β-catenin levels.
2. Understand the role of Wnt signaling in cellular processes during embryo development
The Wnt/β-catenin pathway regulates progenitor expansion, proliferation, fate specification and differentiation. Our focus is to determine how Wnt/β-catenin signaling controls cellular processes such as cell fate determination and proliferation and contractility in collaboration with Dr. E. Ehler, by investigating the role of differential cytoplasmic localization and how signaling activation controls the function of proteins.
In Xenopus laevis, we have implicated CK2 and GSK3β in regulating dorsal fate determination. Currently, we aim to determine how these two kinases are regulated endogenously during early Xenopus laevis development and during oogenesis. In the mouse, through the study of CK2α ablated embryos, we have implicated CK2 in regulating cellular proliferation. We are pursuing biochemical, molecular and genetic approaches to determine the downstream targets of CK2 during cell proliferation in vivo.
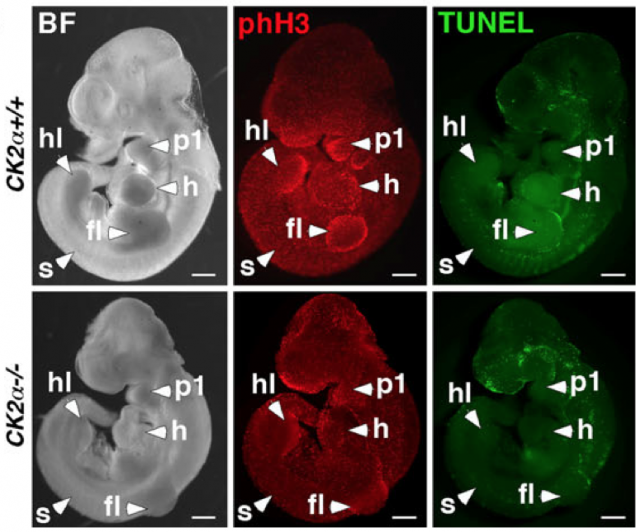
Proliferation and apoptosis in E10.5 CK2alpha-/- embryos stained by WIHC for phH3 (middle pannel) and TUNEL (right pannel). Photographs show bright field (BF), PhH3 and TUNEL staining.0.5 mm. Abbreviations: fl forelimb bud, h heart, hl hindlimb bud, p1 first pharyngeal arch, s somite (from Dominguez et al. 2008).
3. Determine the role of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway during organ development and maintenance, such as heart formation
Wnt signaling is essential for heart development and is proposed to be involved in congenital heart disease. We have shown that CK2α is essential for proper heart formation. We are now dissecting the mechanism(s) that CK2α utilizes to control heart development. We are studying precise localization of Wnt/β-catenin activation and determine the downstream targets of CK2 during cardiogenesis in vivo. Understanding how deficient Wnt/β-catenin signaling leads to embryonic malformations will help develop strategies to prevent or correct defects in morphogenetic processes that lead to congenital heart defects.

CK2α (Csnk2a1) homozygous mutant mice die by embryonic day (E)11 and display defects in the heart, neural tube, pharyngeal arches, tailbud and somites.
SELECTED PUBLICATIONS:
Ortega C, Seidner Y, and Dominguez I. Mining CK2 in cancer. PLOS ONE 2014 Dec 26;9(12):e115609
Siriwardana NS, Meyer R, Havasi A, Dominguez I, Panchenko MV. Cell cycle-dependent chromatin shuttling of HBO1-JADE1 histone acetyl transferase (HAT) complex. Cell Cycle. 2014 Apr 16;13(12)
Iskratsch T., Reijntjes S., Dwyer, J., Toselli P., Degano I.R.,Dominguez I. and Ehler E. Two distinct phosphorylation events govern the function of muscle FHOD3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013, 70(5):893-908
Papanicolaou K.N., Kikuchi R., Ngoh G.A., Coughlan K.A.,Dominguez I., Stanley W.C., Walsh K. Mitofusins 1 and 2 are essential for postnatal metabolic remodeling in heart. Circ. Res. 2012; 111(8):1012-26
Imbrie, G.A., Wu H., Seldin, D.C. Dominguez, I. Asymmetric localization of CK2α during Xenopus oogenesis. Human Genet Embryol 2012; S4:001
Dominguez I (Corresponding author), Degano IR, Chea K, Toselli P, Seldin DC. CK2α is Essential for Embryonic Morphogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Oct; 356(1-2): 209-16
Currier N., Chea K., Hlavacova M., Sussman D.J., Seldin D.C.Dominguez I. Dynamic expression of a LEF-EGFP Wnt reporter in mouse development and cancer. Genesis 2010 Mar; 48(3): 183-94
Wu H, Symes K, Seldin DC, Dominguez I. Threonine 393 of β-catenin regulates interaction with Axin. J Cell Biochem. 2009; Sep 1;108(1):52-63
Seldin DC (Corresponding author), Lou DY, Toselli P, Landesman-Bollag E, Dominguez I. Gene targeting of CK2 catalytic subunits. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008; 316 (1-2):141-7
Bryja V., Schambony A., Čajánek L., Dominguez I., Arenas, E. Schulte G. β-arrestin and casein kinase 1/2 define distinct branches of non-canonical WNT signaling pathways. EMBO Rep.2008; 9(12):1244-50
Chitalia VC, Foy RL, Bachschmid MM, Zeng L, Panchenko MV, Zhou MI, Bharti A, Seldin DC, Lecker SH, Dominguez I, Cohen HT. Jade-1 inhibits Wnt signaling by ubiquitinating β-catenin and mediates Wnt pathway inhibition by pVHL. Nat Cell Biol. 2008; 10(10):1208-16
Lou DY, Dominguez I, Toselli P, Landesman-Bollag E, O’Brien C, Seldin DC. The alpha catalytic subunit of protein kinase CK2 is required for normal embryonic development Mol. 2008; 28(1):131-9
Seldin DC (Corresponding author), Landesman-Bollag E, Farago M, Currier N, Lou D, Dominguez I. CK2 as a positive regulator of Wnt signaling and tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biochem.2005; 274(1-2):63-7
Dominguez I (Corresponding author), Mizuno J, Wu H, Imbrie GA, Symes K, Seldin DC. A role for CK2α/β in Xenopus early embryonic development, Mol Cell Biochem 2005; 274(1-2):125-31
Currier N, Solomon SE, Demicco EG, Chang DL, Farago M, Ying H, Dominguez I, Sonenshein GE, Cardiff RD, Xiao ZX, Sherr DH, Seldin DC. Oncogenic signaling pathways activated in DMBA-induced mouse mammary tumors Toxicologic Pathology2005; 33(6):726-37
Farago M, Dominguez I, Landesman-Bollag E, Xu X, Rosner A, Cardiff RD, Seldin DC. Kinase inactive GSK3β promotes Wnt signaling and mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Research 2005; 65(13):5792-801
Green JB, Dominguez I, Davidson LA. Self-organization of vertebrate mesoderm based on simple boundary conditions. Dev Dyn 2004; 31(3):576-81
Dominguez I (Corresponding author), Mizuno J, Wu H, Song DH, Symes K, Seldin DC. Protein kinase CK2 is required for dorsal axis formation in Xenopus embryos. Dev Biol 2004; 274(1):110-24
Song DH, Dominguez I, Mizuno J, Kaut M, Mohr S”C, Seldin DC. CK2 Phosphorylation of the armadillo repeat region of β-catenin potenciates Wnt signaling J Biol Chem 2003; 278(26):24018-25
Dominguez I, Green JB. Dorsal downregulation of GSK3b by a non-Wnt-like mechanism is an early molecular consequence of cortical rotation in early Xenopus embryos. Development 2000; 127(4): 861-8
These results on Wnt/β-catenin signaling in Xenopus early development are included in the textbook “Analysis of Biological Development” by Klaus Kalthoff, published by McGraw-Hill.
Dominguez I (Co-first author), Itoh K, Sokol SY. Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3β as a negative regulator of dorsoventral axis formation in Xenopus embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92(18): 8498-502
Martínez-Gimeno C, Díaz-Meco MT, Domínguez I, Moscat J. Alterations in levels of different protein kinase C isotypes and their influence on behavior of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: epsilon PKC, a novel prognostic factor for relapse and survival. Head Neck. 1995; 17(6):516-25
Sanz L, Berra E, Municio MM, Dominguez I, Lozano J, Johansen T, Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT. ζ PKC plays a critical role during stromelysin promoter activation by platelet-derived growth factor through a novel palindromic element. J Biol Chem 1994; 269(13):10044-9
Lozano J, Berra E, Municio MM, Diaz-Meco MT, Dominguez I, Sanz L, Moscat J. Protein kinase C ζ isoform is critical for kappa β-dependent promoter activation by phingomyelinase. J Biol Chem 1994; 269(30):19200-2
Diaz-Meco MT, Dominguez I (Co-first author), Sanz L, Dent P, Lozano J, Municio MM, Berra E, Hay RT, Sturgill TW, Moscat J. ζ PKC induces phosphorylation and inactivation of I kappa β-α in vitro. EMBO J 1994; 13(12):2842-8
Diaz-Meco MT, Berra E, Municio MM, Sanz L, Lozano J,Dominguez I, Diaz-Golpe V, Lain de Lera MT, Alcamí J, Payá CV, Moscat J. A dominant negative protein kinase C ζ subspecies blocks NF-κ B activation. Mol Cell Biol 1993; 13(8):4770-5
Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Fernandez B, Dominguez I, Jacqué JM, Thomas D, Diaz-Meco MT, Moscat J, Virelizier JL. Phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis activates NF-κB and increases human immunodeficiency virus replication in human monocytes and T lymphocytes. J Virol 1993; 67(11):6596-604
Berra E, Diaz-Meco MT, Dominguez I (Co-first author), Municio MM, Sanz L, Lozano J, Chapkin RS, Moscat J. Protein kinase C ζ isoform is critical for mitogenic signal transduction. Cell 1993; 74(3):555-63
Dominguez I (Co-first author), Sanz L, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Diaz-Meco MT, Virelizier JL, Moscat J. Inhibition of protein kinase C ζ subspecies blocks the activation of an NF-κ B-like activity in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol 1993; 13(2):1290-5
Dominguez I, Diaz-Meco MT, Municio MM, Berra E, García de Herreros A, Cornet ME, Sanz L, Moscat J. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C ζ subspecies in maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol 1992; 12(9):3776-83
Diaz-Meco MT, Dominguez I (Co-first author), Sanz L, Municio MM, Berra E, Cornet ME, Garcia de Herreros A, Johansen T, Moscat J. Phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidyl-choline is a target of transforming growth factor β 1 inhibitory signals. Mol Cell Biol 1992; 12(1):302-8
Dominguez I, Marshall MS, Gibbs JB, García de Herreros A, Cornet ME, Graziani G, Diaz-Meco MT, Johansen T, McCormick F, Moscat J. Role of GTPase activating protein in mitogenic signalling through phosphatidylcholine-
García de Herreros A, Dominguez I, Diaz-Meco MT, Graziani G, Cornett ME, Guddal PH, Johansen T, Moscat J. Requirement of phospholipase C-catalyzed hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine for maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes in response to insulin and ras p21. J Biol Chem. 1991; 266(11):6825-9
BOOK CHAPTERS:
Revuelta-Cervantes, J, Macias Alvarez, L., Dominguez I. CK2 in embryonic development. The Wiley-IUBMB Series on Biochemistry and Molecular Biology: Protein Kinase CK2. Editor: Lorenzo Pinna. Wiley-Blackwell Publishing. John Wiley & Sons, Inc (2012)
Ortega C, Prince-Wright L, Dominguez I. Role of CK2 in organ formation. Proceedings of the CK2-VII meeting. Editors Khalil Ahmed, Olaf Issinger and Ryszard Szyska (2014)
Apfel J., Parikh J.R., Reischmann P., Ewing R.M., Müller O, Xia Y, Dominguez I. The Wnt signaling network in Cancer. Systems Biology of Cancer. Editor: Sam Thiagalingam. Cambridge University Press (2015)

